Unlocking the Power of ArcGIS Desktop: A Comprehensive Guide to Enhancing Your Geospatial Analysis

ArcGIS Desktop is a powerful tool for geospatial analysis, offering a wide range of features and capabilities. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced user, these 15 tips will help you unlock the full potential of ArcGIS Desktop and streamline your workflow, making your geospatial analysis more efficient and effective.
1. Master the Basics
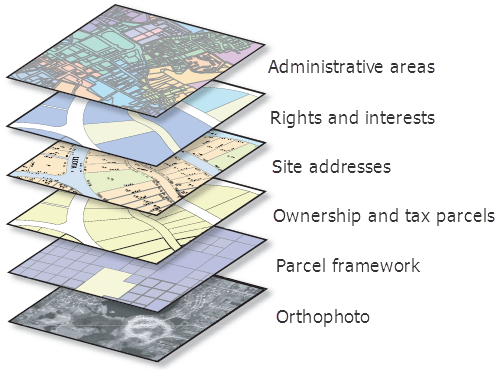
Before diving into advanced techniques, ensure you have a solid understanding of the basic functionalities of ArcGIS Desktop. Familiarize yourself with the interface, toolbars, and navigation. This foundation will make it easier to explore more complex features later.
2. Efficient Data Management

Organize Your Data

Maintain a well-organized data structure. Create separate folders for different projects and keep your data files, shapefiles, and attribute tables in a logical hierarchy. This will make it easier to locate and manage your data.
Use Data Interoperability
ArcGIS Desktop supports various data formats. Leverage the Data Interoperability tool to import and export data, ensuring compatibility with other software and systems. This tool can handle a wide range of formats, including CAD, GIS, and database files.
3. Enhance Your Map Visualizations

Symbolize Your Data
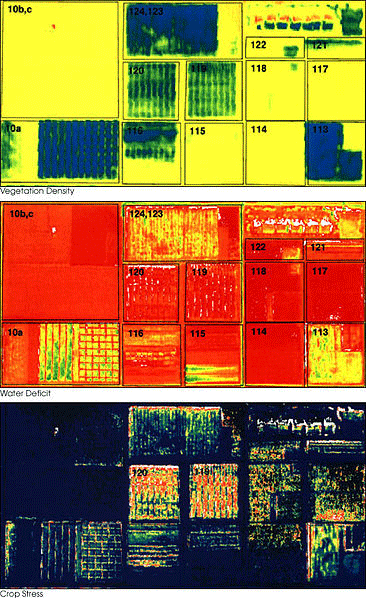
Utilize the Symbol Level Drawing (SLD) feature to create visually appealing and informative maps. SLD allows you to control the appearance of your data, including line thickness, point size, and color schemes. This enhances the clarity and impact of your maps.
Use Map Templates
Save time by creating and using map templates. Map templates allow you to define a standard layout, including title, legend, and scale bar, which can be applied to new maps. This ensures consistency across your projects and saves you from repetitive tasks.
4. Efficient Data Analysis

Utilize Spatial Statistics

ArcGIS Desktop offers a range of spatial statistics tools for analyzing your data. These tools can help you identify patterns, clusters, and outliers in your geospatial data. By understanding these patterns, you can make more informed decisions and draw meaningful insights.
Leverage Geoprocessing Tools
Geoprocessing tools are powerful instruments for data manipulation and analysis. They allow you to perform tasks such as buffering, clipping, and merging data. Explore the various geoprocessing tools available and learn how to automate repetitive tasks to save time and effort.
5. Optimize Your Map Composition

Choose the Right Map Projections
Select the appropriate map projection for your data. Different projections are suitable for different purposes, such as accurate area representation or direction preservation. Choose the projection that best aligns with your analysis goals.
Use Map Layouts Effectively
Create visually appealing and informative map layouts. Experiment with different layout options, such as adding a north arrow, scale bar, and title. Consider using map elements like gradients, shadows, and textures to enhance the visual impact of your maps.
6. Efficient Data Sharing

Utilize Web Maps

Share your maps and data with others by creating web maps. ArcGIS Desktop allows you to publish your maps to ArcGIS Online or Portal for ArcGIS. This enables collaboration and provides easy access to your geospatial information.
Leverage Web Services

Web services, such as WMS and WFS, allow you to share your data with other users and applications. By exposing your data as web services, you can ensure that it is accessible and reusable across different platforms and systems.
7. Master Symbology and Labeling

Custom Symbol Creation
Create custom symbols to represent your data uniquely. ArcGIS Desktop offers a wide range of symbol options, including simple markers, filled symbols, and cartographic line symbols. Experiment with different styles to enhance the visual representation of your data.
Effective Labeling Techniques
Labels are essential for communicating information on your maps. Use clear and concise labels, and consider using callouts to highlight specific features. Experiment with different font styles, sizes, and colors to ensure your labels are readable and aesthetically pleasing.
8. Efficient Data Editing

Use Editing Templates
Create editing templates to streamline your data editing process. Editing templates define the fields, attributes, and symbology for new features, ensuring consistency and reducing errors. This is especially useful when working with large datasets.
Utilize the Editing Toolbar
The Editing toolbar provides a range of tools for efficient data editing. Familiarize yourself with tools like the Feature Construction tool, which allows you to create new features by snapping to existing ones, and the Attribute Editor, which enables you to modify feature attributes quickly.
9. Leverage Python for Automation

Automate Tasks with Python
Python scripting can automate repetitive tasks, saving you time and effort. ArcGIS Desktop provides extensive Python support, allowing you to write scripts to perform tasks such as data conversion, geoprocessing, and map creation. This is particularly useful for large-scale projects.
Learn ArcGIS API for Python
The ArcGIS API for Python is a powerful tool for working with geospatial data in Python. It provides a comprehensive set of functions and classes for data analysis, visualization, and map creation. By learning this API, you can unlock the full potential of Python for geospatial tasks.
10. Effective Data Exploration
Utilize the Attribute Table
The Attribute Table is a powerful tool for exploring and analyzing your data. It provides a detailed view of your feature attributes, allowing you to sort, filter, and query your data. Use the Attribute Table to gain insights into your data and identify patterns or outliers.
Visualize Data with Charts
ArcGIS Desktop offers a range of chart types for visualizing your data. These charts can help you identify trends, patterns, and relationships in your data. Experiment with different chart types, such as bar charts, line charts, and pie charts, to find the most effective way to communicate your data.
11. Optimize Your Map Performance
Manage Map Drawing
Optimize your map drawing performance by adjusting the drawing settings. Consider using simplified representations for large datasets to reduce processing time. This can be especially useful when working with complex maps or large areas.
Utilize Map Tips
Map Tips provide additional information about features when you hover over them. This can be a useful way to quickly access attribute data without opening the Attribute Table. Customize your Map Tips to display the most relevant information for your analysis.
12. Master Advanced Geoprocessing
Understand ModelBuilder
ModelBuilder is a powerful tool for creating and automating geoprocessing workflows. It allows you to build and visualize models, which can be used to perform complex geoprocessing tasks. Learn how to use ModelBuilder to streamline your geoprocessing operations.
Explore Geoprocessing Wizard
The Geoprocessing Wizard provides a user-friendly interface for creating geoprocessing models. It guides you through the process of selecting inputs, defining parameters, and specifying output locations. This is an excellent way to learn about geoprocessing and create custom tools.
13. Efficient Data Export
Export Data in Multiple Formats
ArcGIS Desktop supports a wide range of data export formats. When exporting data, consider the intended use and choose the most appropriate format. For example, use shapefiles for GIS applications and KML for Google Earth.
Use Data Driven Pages
Data Driven Pages allow you to create multiple maps from a single data source. This is particularly useful when creating maps for different regions or time periods. By using Data Driven Pages, you can export a series of maps efficiently and consistently.
14. Leverage ArcGIS Pro
Discover ArcGIS Pro’s Features
ArcGIS Pro is the latest ArcGIS Desktop application, offering advanced features and improved performance. Explore the capabilities of ArcGIS Pro, such as its modern interface, 3D visualization, and improved geoprocessing tools. Consider upgrading to ArcGIS Pro for a more powerful geospatial analysis experience.
Learn the Differences
While ArcGIS Pro offers many similarities to ArcMap, it also has unique features and a different workflow. Take the time to learn the differences between the two applications, such as the new ribbon interface and the Project-based approach in ArcGIS Pro. This will help you transition smoothly and take advantage of the new capabilities.
15. Stay Updated with Training and Resources
Explore Training Options
ArcGIS Desktop offers a range of training resources to help you improve your skills. Explore online courses, webinars, and tutorials to learn new techniques and stay up-to-date with the latest features. Continuous learning will enhance your geospatial analysis capabilities.
Utilize Community Resources
The ArcGIS user community is a valuable resource for learning and collaboration. Join online forums, attend user conferences, and connect with other professionals. Sharing knowledge and experiences with the community can provide valuable insights and new ideas for your geospatial analysis projects.
Conclusion
By implementing these 15 tips, you can enhance your geospatial analysis skills and streamline your workflow in ArcGIS Desktop. From efficient data management to advanced geoprocessing and data sharing, these techniques will help you unlock the full potential of this powerful software. Remember to continuously explore new features, stay updated with training, and leverage the vast resources available to become an expert in geospatial analysis.
FAQ
What is the best way to organize my data in ArcGIS Desktop?
+Organizing your data in ArcGIS Desktop is crucial for efficient management. Create separate folders for different projects and maintain a logical hierarchy. This will help you locate and manage your data effectively.
How can I create visually appealing maps in ArcGIS Desktop?
+To create visually appealing maps, utilize the Symbol Level Drawing (SLD) feature to control the appearance of your data. Experiment with different symbol styles, colors, and map layouts to enhance the visual impact of your maps.
What are some effective ways to share my maps and data with others?
+You can share your maps and data by creating web maps and publishing them to ArcGIS Online or Portal for ArcGIS. Additionally, you can expose your data as web services, such as WMS and WFS, to ensure accessibility and reusability.
How can I automate repetitive tasks in ArcGIS Desktop?
+Python scripting is a powerful tool for automating tasks in ArcGIS Desktop. Write scripts to perform data conversion, geoprocessing, and map creation. Additionally, explore the ArcGIS API for Python to unlock advanced capabilities.
What are some best practices for data exploration in ArcGIS Desktop?
+Utilize the Attribute Table to explore and analyze your data. Sort, filter, and query your data to gain insights. Additionally, visualize your data with charts to identify trends and relationships.