Introduction

In today’s data-driven world, the ability to visualize information effectively is more crucial than ever. Data visualization is a powerful tool that helps us understand complex datasets, identify patterns, and communicate insights clearly. Whether you’re a data analyst, a business professional, or a student, mastering the art of data visualization can greatly enhance your skills and make your work more impactful. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore 15 different ways to visualize your data, providing you with a diverse toolkit to choose from based on your specific needs and goals. From classic charts to innovative visual representations, we’ll cover a wide range of options to ensure you can effectively present your data and tell compelling stories.
1. Bar Charts
Bar charts are one of the most common and versatile types of data visualization. They are ideal for comparing different categories or groups, especially when you want to highlight the differences between them. Each category is represented by a bar, with the length of the bar indicating the value or frequency. Bar charts can be horizontal or vertical, and they are particularly useful for showing changes over time or for making comparisons between different variables.
2. Line Charts
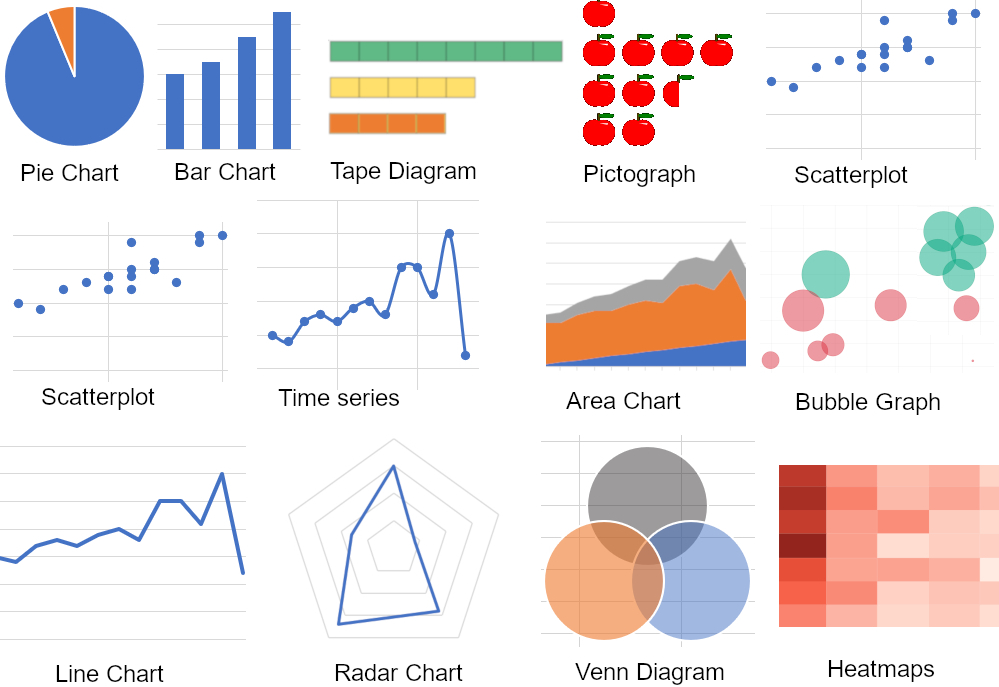
Line charts are perfect for displaying trends and changes over time. They connect data points with a line, making it easy to identify patterns, trends, and correlations. Line charts are often used to visualize time series data, such as sales figures over the course of a year or temperature changes throughout the seasons. By connecting the data points, line charts provide a smooth and continuous representation of the data, making it simple to spot any fluctuations or trends.
3. Area Charts
Area charts are similar to line charts but with an additional layer of shading between the line and the x-axis. This shading emphasizes the area under the line, making it easier to visualize the cumulative effect of the data. Area charts are particularly useful when you want to highlight the total or cumulative value of a series over time. They can effectively showcase the growth or decline of a particular metric, making it ideal for tracking progress or comparing multiple series.
4. Pie Charts
Pie charts are a classic way to represent the composition of a whole. They divide a circle into segments, with each segment representing a category and its proportion in the whole. Pie charts are best used when you want to show the distribution of a dataset among a small number of categories. They are visually appealing and can quickly convey the relative sizes of each category. However, it’s important to note that pie charts may not be the best choice for comparing multiple categories, as they can become cluttered and difficult to interpret.
5. Donut Charts
Donut charts are a variation of pie charts, offering a more modern and visually appealing alternative. Like pie charts, they divide a circular space into segments, but with a central hole. Donut charts are great for displaying the composition of a whole while also providing a visual representation of the central category or value. They can effectively showcase the distribution of data while also highlighting the relationship between the categories. Donut charts are often used when you want to emphasize both the individual categories and their combined effect.
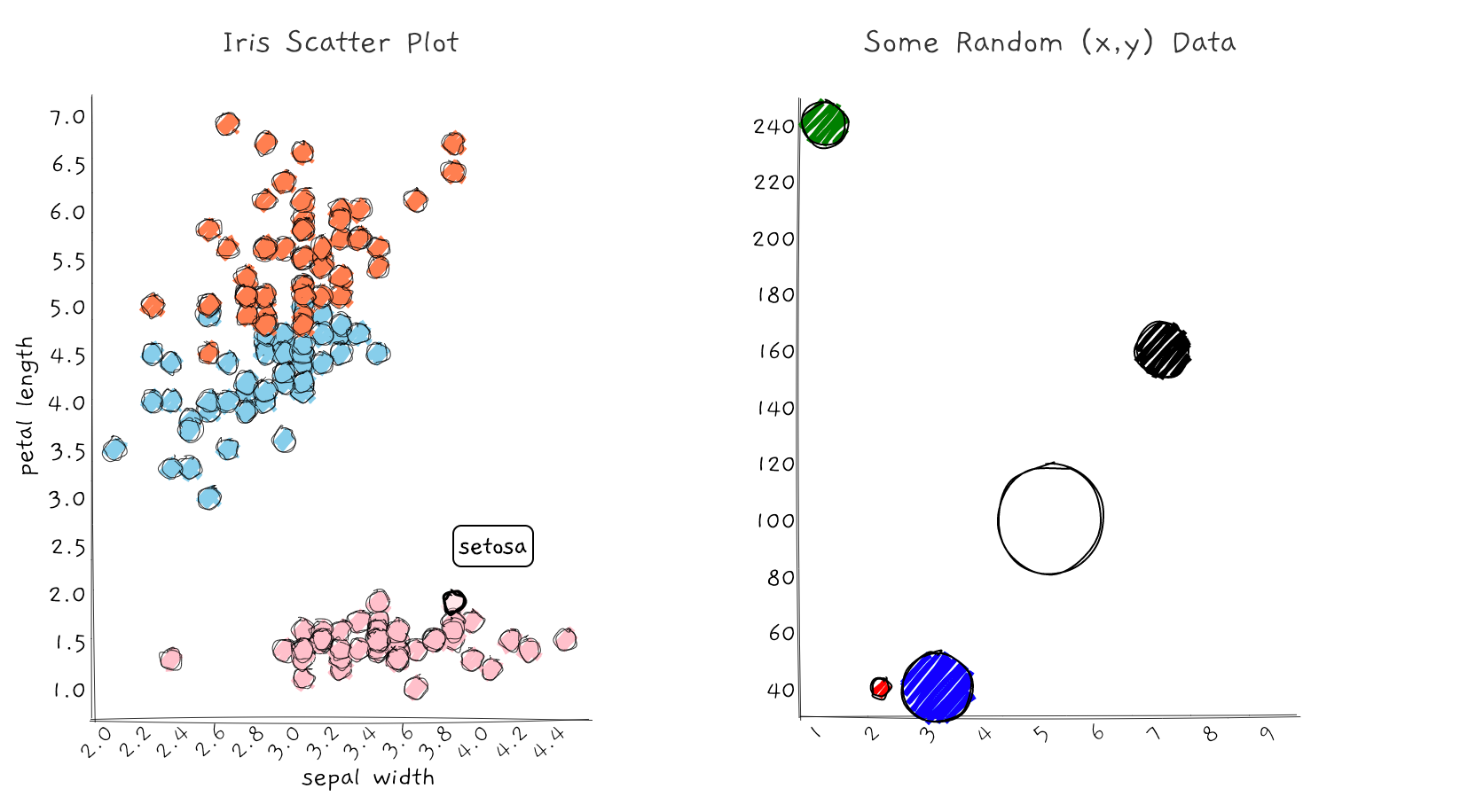
6. Scatter Plots

Scatter plots are an excellent choice for visualizing the relationship between two numerical variables. Each data point is represented by a dot or marker, and its position on the plot indicates the values of the two variables. Scatter plots are particularly useful for identifying patterns, correlations, and outliers in your data. By plotting the data points, you can quickly see if there is a positive, negative, or no correlation between the variables. Scatter plots are versatile and can be used for a wide range of datasets, making them a valuable tool in data analysis.
7. Bubble Charts
Bubble charts are an extension of scatter plots, adding an additional dimension to the visualization. In addition to the x and y-axis, bubble charts include a third variable represented by the size of the bubbles. This allows you to display three dimensions of data in a single chart. Bubble charts are ideal for comparing multiple variables simultaneously and can help identify patterns or relationships that may not be apparent in traditional scatter plots. They are particularly useful when you want to highlight the importance or impact of each data point based on its size.
8. Heatmaps
Heatmaps are powerful tools for visualizing the relationship between two or more variables. They use a color-coded matrix to represent the values of the variables, with each cell in the matrix representing a combination of the variables. The color intensity or hue indicates the value or frequency of the data. Heatmaps are excellent for identifying patterns, clusters, and correlations within your data. By using a color scale, heatmaps provide a visually appealing and intuitive way to understand complex relationships between variables.
9. Box Plots
Box plots, also known as box-and-whisker plots, are a simple yet effective way to visualize the distribution of a dataset. They provide a five-number summary of the data, including the minimum, first quartile, median, third quartile, and maximum. Box plots are particularly useful for comparing the distribution of multiple datasets or for identifying outliers. By displaying the range and variability of the data, box plots offer a quick and efficient way to understand the shape and spread of your dataset.
10. Histogram
Histograms are a type of bar chart used to represent the distribution of continuous data. They divide the data into bins or intervals and display the frequency or count of data points within each bin. Histograms are excellent for understanding the shape and spread of a dataset, as well as identifying any patterns or anomalies. By grouping the data into bins, histograms provide a clear visualization of the distribution, making it easier to identify any skewness or multimodality.
11. Treemap
Treemaps are a unique and visually appealing way to represent hierarchical data. They use nested rectangles to display the structure and composition of the data. Each rectangle represents a category or node, and its size is proportional to its value or frequency. Treemaps are ideal for exploring large datasets with multiple levels of hierarchy, such as file systems or organizational structures. By using color and size, treemaps provide a clear and concise visualization of the data, making it easy to identify the most significant categories or nodes.
12. Network Graphs
Network graphs, also known as node-link diagrams, are used to visualize relationships between entities. They represent entities as nodes (circles or other shapes) and connections as links or edges. Network graphs are particularly useful for understanding complex systems, social networks, or any dataset with interconnected relationships. By visualizing the connections between nodes, network graphs provide insights into the structure and dynamics of the network, helping you identify key players, clusters, or patterns within the data.
13. Choropleth Maps
Choropleth maps are a powerful tool for visualizing geographic data. They use color-coded regions or areas to represent the values of a particular variable across a geographic space. Each region or area is colored based on the value of the variable, allowing you to quickly identify patterns, trends, or differences across different locations. Choropleth maps are ideal for displaying data such as population density, election results, or climate data, providing a visual representation of the distribution of the variable across a geographic area.
14. Word Clouds
Word clouds, or tag clouds, are a creative way to visualize text data. They display the frequency of words or phrases in a dataset by varying their size and placement. The more frequent a word is, the larger and more prominent it appears in the word cloud. Word clouds are excellent for quickly understanding the most common themes or topics within a text corpus. They provide a visual summary of the text, making it easy to identify the most significant words or phrases at a glance.
15. Gantt Charts
Gantt charts are specifically designed for project management and scheduling. They use a horizontal bar chart to represent tasks or activities, with the length of the bar indicating the duration of the task. Gantt charts are particularly useful for visualizing project timelines, dependencies, and progress. By displaying the start and end dates of each task, Gantt charts provide a clear overview of the project schedule, making it easier to identify any potential delays or conflicts.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored 15 different ways to visualize your data, each with its own unique strengths and applications. From classic charts like bar charts and line charts to more innovative visualizations like treemaps and network graphs, you now have a diverse toolkit to choose from. By selecting the right visualization for your data, you can effectively communicate your insights, identify patterns, and make informed decisions. Remember, the key to successful data visualization is understanding your data and choosing the most appropriate representation to tell your story.