Getting Started with Qualitative Data Analysis

Qualitative data analysis is a process that involves exploring, understanding, and interpreting non-numerical data to gain insights and make meaningful conclusions. It is a valuable tool for researchers, analysts, and professionals across various fields, including social sciences, market research, and healthcare. In this comprehensive guide, we will cover 18 practical tips to help you excel in qualitative data analysis, ensuring you can extract valuable information and draw accurate conclusions from your data.
1. Define Your Research Objectives

Before diving into qualitative data analysis, it is crucial to clearly define your research objectives. Understand the specific questions or problems you aim to address through your analysis. This will guide your data collection, coding, and interpretation processes, ensuring a focused and meaningful approach.
2. Choose an Appropriate Research Design
Select a research design that aligns with your objectives and the nature of your data. Consider whether you need a case study, ethnographic research, grounded theory, or another qualitative research approach. Each design has its strengths and limitations, so choose wisely based on your research goals.
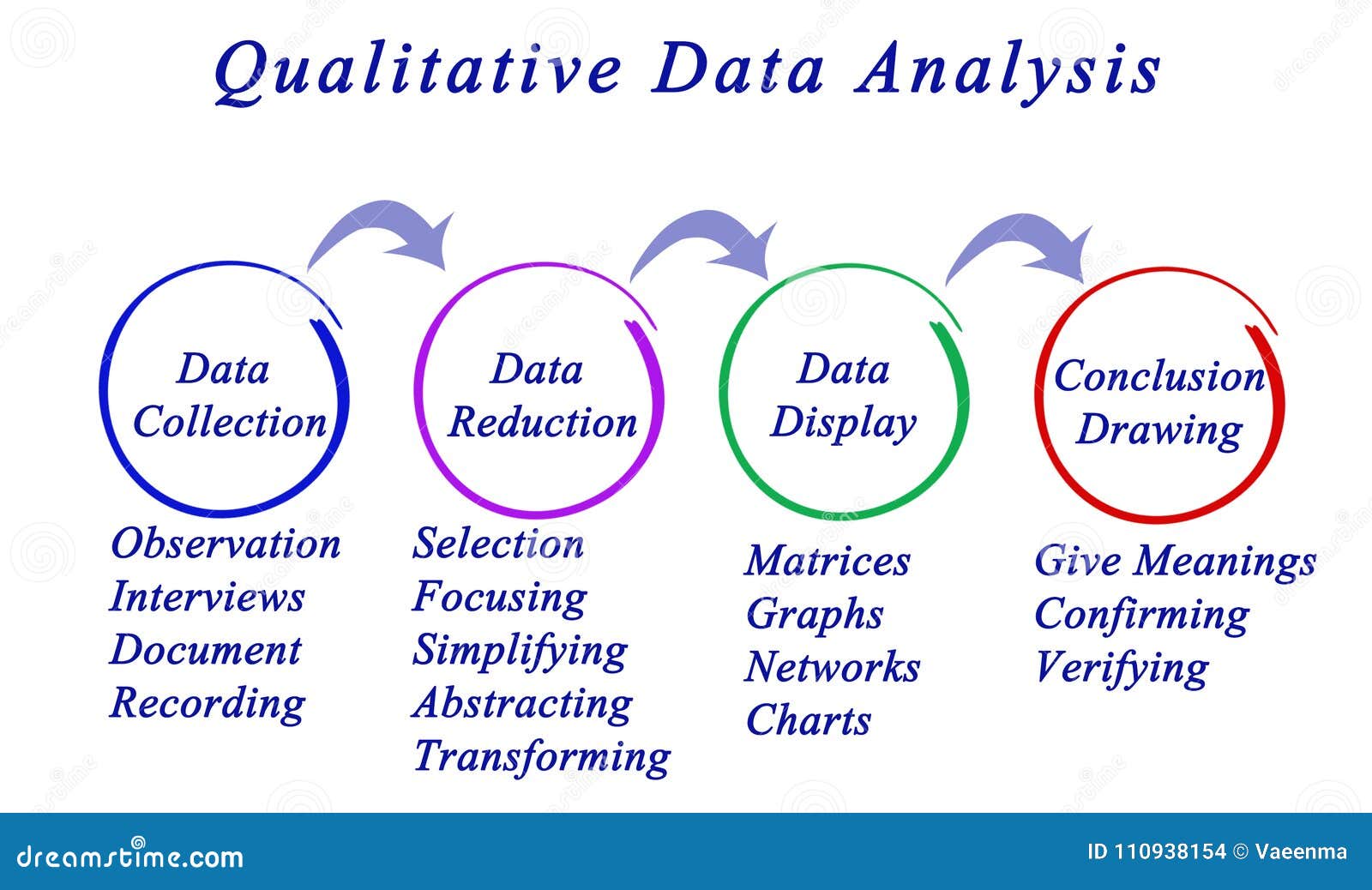
3. Collect Rich and Diverse Data

Qualitative data analysis thrives on rich and diverse data. Collect a variety of data sources, such as interviews, focus groups, observations, and documents. Ensure your data collection methods capture the perspectives and experiences of your participants or subjects accurately.
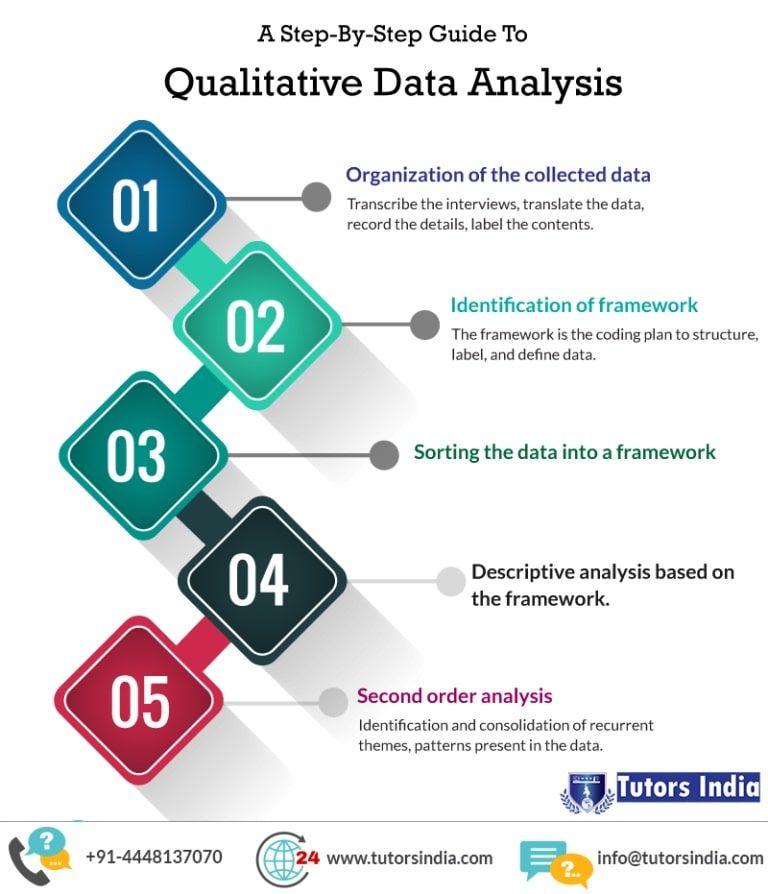
4. Transcribe and Prepare Your Data

Transcribe any audio or video recordings into written form. This step is crucial for easy access and analysis of your data. Prepare your data by organizing it into a format that suits your analysis software or tools. Clean and anonymize your data to protect participant confidentiality.
5. Familiarize Yourself with the Data

Take time to read through your transcripts, notes, and observations. Familiarize yourself with the content, themes, and patterns that emerge. This initial exploration will help you develop a deeper understanding of your data and identify potential areas of focus for further analysis.
6. Develop a Coding Scheme

Coding is a fundamental step in qualitative data analysis. Develop a coding scheme that categorizes and labels your data. Create a list of codes that represent key concepts, themes, or patterns you identify in your data. Ensure your coding scheme is comprehensive, yet flexible, to accommodate new insights as you analyze.
7. Apply Coding Consistency

Consistency is vital in qualitative data analysis. Ensure that you apply your coding scheme consistently across all your data. Train multiple coders, if possible, to enhance reliability and reduce bias. Regularly discuss and resolve any coding discrepancies to maintain a high level of accuracy.
8. Use Software for Efficient Analysis

Leverage qualitative data analysis software to streamline your work. Tools like MAXQDA, NVivo, or ATLAS.ti offer features for coding, organizing, and visualizing your data. These software programs can save you time and effort, especially when dealing with large datasets.
9. Explore Different Coding Techniques
Qualitative data analysis offers various coding techniques, such as open coding, axial coding, and focused coding. Experiment with different techniques to find the ones that best suit your data and research objectives. Each technique has its advantages, so be open to exploring multiple approaches.
10. Immerse Yourself in the Data

Immerse yourself in your data to gain a deeper understanding. Read and re-read your transcripts, notes, and observations. Look for patterns, connections, and emerging themes. This immersive approach will help you develop a holistic view of your data and identify nuances that might otherwise be missed.
11. Conduct Member Checks
Member checks involve sharing your preliminary findings with participants to validate your interpretations. This step ensures that your analysis aligns with the experiences and perspectives of your participants. It adds credibility to your research and demonstrates respect for their contributions.
12. Triangulate Your Data
Triangulation involves using multiple data sources or methods to cross-validate your findings. Collect data from various sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, to ensure the reliability and validity of your analysis. Triangulation strengthens your conclusions and enhances the overall quality of your research.
13. Engage in Peer de-Briefing
Peer de-briefing is a valuable practice where you discuss your analysis process and findings with colleagues or peers. This collaborative approach provides fresh perspectives, identifies potential biases, and helps refine your analysis. It ensures a more comprehensive and accurate interpretation of your data.
14. Analyze Context and Culture
Qualitative data analysis should consider the context and cultural background of your participants. Understand the social, cultural, and historical factors that shape their experiences and perspectives. This contextual analysis adds depth and richness to your interpretations.
15. Identify Emerging Themes
As you analyze your data, look for emerging themes and patterns. These themes may not be apparent initially but can provide valuable insights into your research questions. Identify and label these themes, and explore their significance in relation to your research objectives.
16. Create Visual Representations
Visual representations, such as concept maps or mind maps, can help you organize and understand your data more effectively. These visual tools provide a bird’s-eye view of your analysis, making it easier to identify connections, relationships, and potential areas for further exploration.
17. Write Memos and Reflective Notes
Throughout your analysis, write memos and reflective notes to document your thoughts, insights, and decisions. These notes serve as a record of your analytical journey and can be invaluable when writing up your findings. They also help you maintain a transparent and traceable analysis process.
18. Draw Meaningful Conclusions
Finally, draw meaningful conclusions from your qualitative data analysis. Summarize your key findings, highlighting the most significant insights and their implications. Ensure your conclusions are supported by your data and align with your research objectives. Write a clear and concise report or paper that communicates your results effectively.
Notes

- Remember that qualitative data analysis is an iterative process. Be prepared to revisit and refine your analysis as new insights emerge.
- Stay open-minded and flexible throughout your analysis. Qualitative data often reveals unexpected findings, so be willing to adjust your research direction accordingly.
- Continuously reflect on your own biases and assumptions to ensure a fair and unbiased analysis.
- Collaborate with colleagues or seek feedback from experts to enhance the quality and validity of your analysis.
Final Thoughts

Qualitative data analysis is a powerful tool for uncovering valuable insights and understanding complex phenomena. By following these 18 tips, you can enhance your qualitative analysis skills and produce meaningful and reliable findings. Remember that practice and experience are key to mastering this art, so embrace the challenges and enjoy the process of uncovering hidden gems within your data.
FAQ

What is qualitative data analysis, and why is it important?
+Qualitative data analysis is a method used to understand and interpret non-numerical data, such as text, images, and observations. It is important because it allows researchers to gain deep insights into complex phenomena, uncover hidden patterns, and develop a comprehensive understanding of human experiences and behaviors.
How do I choose the right research design for my qualitative study?
+The choice of research design depends on your research objectives and the nature of your study. Consider factors such as the research question, the depth of exploration required, and the resources available. Common qualitative research designs include case studies, ethnographic research, and grounded theory.
What are some best practices for collecting qualitative data?
+To collect high-quality qualitative data, ensure you have a clear research plan, use appropriate data collection methods (e.g., interviews, focus groups), and create a comfortable and safe environment for participants to share their experiences. Maintain ethical standards and ensure participant confidentiality.
How can I ensure coding consistency in my qualitative analysis?
+Coding consistency is crucial for reliable qualitative analysis. Develop a clear and comprehensive coding scheme, train multiple coders if possible, and regularly discuss and resolve coding discrepancies. Regularly review and refine your coding process to maintain consistency throughout your analysis.
What are some common challenges in qualitative data analysis, and how can I overcome them?
+Common challenges include managing large datasets, maintaining coding consistency, and avoiding bias. To overcome these challenges, use qualitative data analysis software, develop a clear coding scheme, engage in peer de-briefing, and continuously reflect on your own biases and assumptions.