1. Define Your Research Objectives and Questions

Before diving into qualitative analysis, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of your research objectives and the specific questions you aim to answer. This step sets the foundation for your entire analysis process. Start by identifying the key aspects you want to explore and the insights you hope to gain. By defining your objectives, you can ensure that your analysis remains focused and targeted, allowing you to extract meaningful conclusions.
2. Choose an Appropriate Research Methodology

Qualitative research encompasses various methodologies, each with its unique approach. When designing your analysis, carefully select the methodology that aligns with your research objectives. Some common methodologies include phenomenology, grounded theory, ethnography, and case studies. Each methodology has its strengths and is suitable for different research contexts. Consider factors such as the nature of your research question, the population you’re studying, and the depth of exploration required.
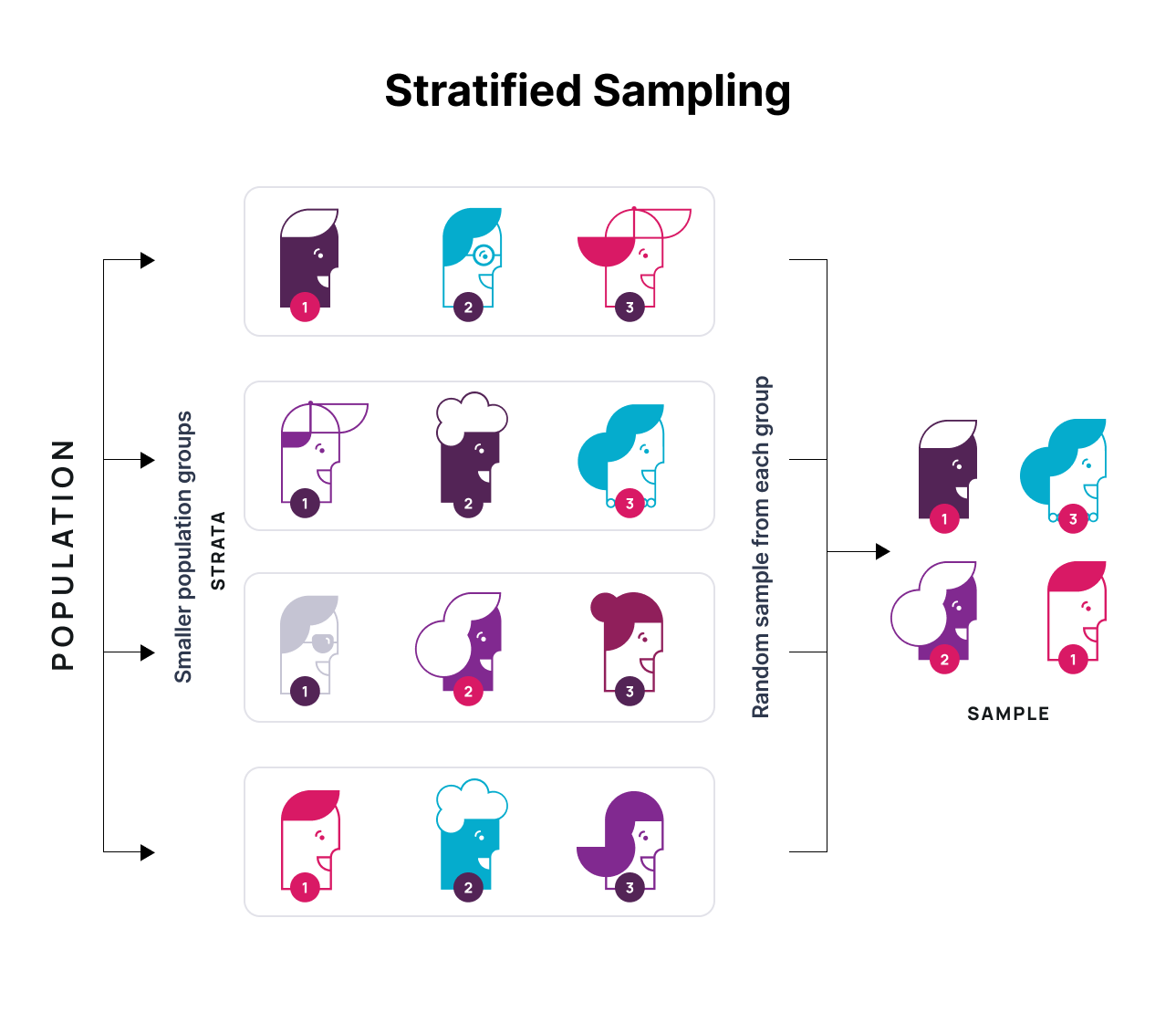
3. Develop a Rigorous Sampling Strategy

A well-designed sampling strategy is essential for obtaining a representative and diverse sample of participants or data sources. In qualitative research, it’s often more effective to select a smaller, carefully chosen sample rather than a large, random one. Consider employing techniques like purposeful sampling, where you deliberately select participants based on specific criteria relevant to your research. This ensures that you gather rich and varied data, enhancing the depth of your analysis.
4. Create a Structured Data Collection Plan

To ensure a systematic and comprehensive data collection process, develop a detailed plan outlining the methods and tools you’ll use. This plan should include the research instruments, such as interview guides, observation protocols, or focus group discussion topics. Clearly define the steps involved in data collection, considering factors like the timing, location, and any specific requirements or ethical considerations. A well-structured plan not only streamlines the data collection process but also enhances the quality and consistency of your data.
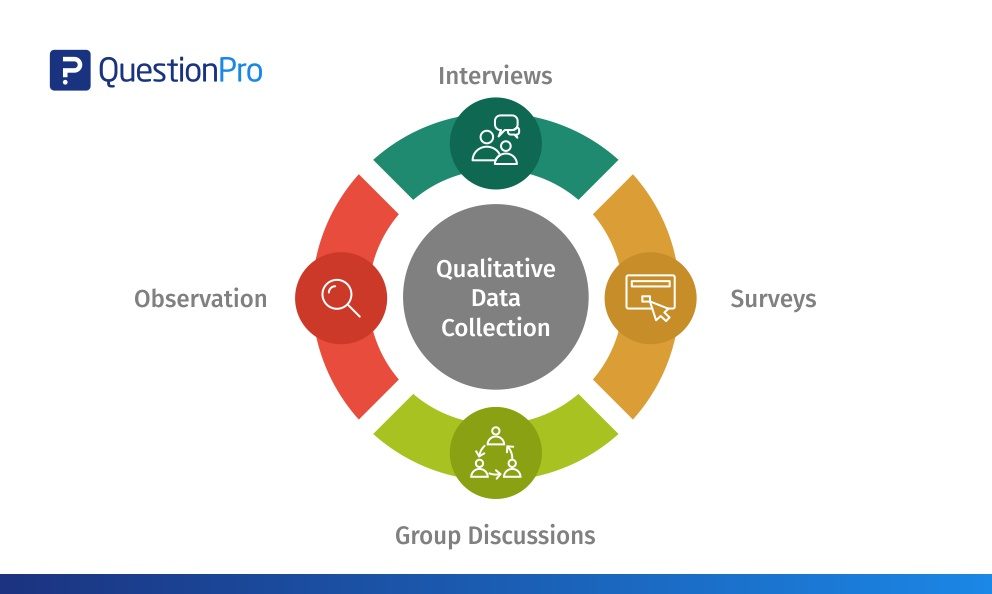
5. Employ Multiple Data Collection Methods

Qualitative research often benefits from the use of multiple data collection methods. By employing a combination of techniques, you can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the research topic. For example, you might conduct in-depth interviews, followed by focus group discussions, and support your findings with observations and document reviews. This approach allows you to cross-validate your data, ensuring the reliability and validity of your analysis.
6. Pay Attention to Ethical Considerations

Ethical considerations are paramount in qualitative research, as they ensure the well-being and privacy of participants. Before initiating your research, obtain the necessary approvals from institutional review boards or ethics committees. Inform participants about the purpose of the research, the potential risks and benefits, and their rights, including the right to withdraw at any time. Obtain informed consent and maintain confidentiality throughout the process. By prioritizing ethical practices, you not only protect your participants but also enhance the credibility of your research.
7. Develop a Robust Data Analysis Framework

A robust data analysis framework is the backbone of your qualitative analysis. Start by familiarizing yourself with the data you’ve collected and identifying emerging themes and patterns. Develop a coding system or framework that organizes your data into meaningful categories. This process, known as thematic analysis, allows you to identify key themes, relationships, and insights within your data. Use software tools or manual coding techniques to assist in the analysis, ensuring a systematic and thorough examination of your data.
8. Write a Compelling Research Report

The final step in your qualitative analysis journey is to communicate your findings effectively through a well-written research report. Structure your report with a clear introduction, methodology section, results, and discussion. Present your findings in a logical and organized manner, supporting them with relevant quotes, observations, or examples from your data. Ensure that your report is accessible to a broad audience, providing a comprehensive yet concise overview of your research.
9. Validate Your Findings and Draw Conclusions

Qualitative research often involves an iterative process of data collection and analysis. As you progress through your analysis, continuously validate your findings by seeking feedback from experts or peers. Engage in reflective practices to ensure the credibility and trustworthiness of your research. Draw conclusions based on the patterns and themes that emerge from your data, ensuring that your interpretations are supported by the evidence you’ve gathered.
10. Utilize Visual Aids and Data Visualization

Visual aids and data visualization techniques can greatly enhance the impact and understanding of your qualitative analysis. Consider using diagrams, charts, or graphs to represent key findings or relationships within your data. These visual representations not only make your report more engaging but also help convey complex information in a simplified manner. Additionally, consider including relevant images or photographs to provide a more immersive experience for your readers.
11. Reflect on the Limitations and Implications
Every research study has its limitations, and it’s important to acknowledge and address them in your analysis. Reflect on the potential biases, sample size, or methodological constraints that may have influenced your findings. By acknowledging these limitations, you demonstrate the transparency and integrity of your research. Additionally, consider the broader implications of your research, such as how your findings contribute to the existing body of knowledge or inform future research directions.
12. Engage in Continuous Learning and Improvement
Qualitative research is an ongoing learning process, and there’s always room for improvement. Stay updated with the latest research methods, techniques, and tools in your field. Attend workshops, conferences, or training sessions to enhance your skills and knowledge. Engage in reflective practice, critically evaluating your own research process and seeking feedback from colleagues or mentors. By continuously learning and improving, you can refine your qualitative analysis skills and contribute to the advancement of your discipline.
Conclusion
Designing a perfect qualitative analysis requires a thoughtful and systematic approach. By defining clear research objectives, selecting an appropriate methodology, and employing rigorous sampling and data collection strategies, you lay the foundation for a successful analysis. Throughout the process, prioritize ethical considerations, develop a robust data analysis framework, and communicate your findings effectively. Remember to validate your results, utilize visual aids, and reflect on the limitations and implications of your research. With dedication and a commitment to continuous learning, you can master the art of qualitative analysis and contribute valuable insights to your field.
FAQ
What are the key differences between qualitative and quantitative research?

+
Qualitative research focuses on exploring and understanding complex phenomena, often using non-numerical data such as interviews, observations, and focus groups. It aims to provide in-depth insights and uncover patterns and themes. Quantitative research, on the other hand, relies on numerical data and statistical analysis to measure and generalize findings. It seeks to establish relationships, test hypotheses, and make predictions.
How can I ensure the reliability and validity of my qualitative research?

+
To ensure reliability and validity, it’s important to follow rigorous research practices. This includes using a clear and well-defined research design, employing appropriate sampling techniques, and maintaining consistency in data collection and analysis. Additionally, triangulation (using multiple data sources or methods) and peer debriefing (seeking feedback from experts) can enhance the credibility of your research.
What are some common challenges in qualitative data analysis, and how can I overcome them?
+
Qualitative data analysis can be challenging due to the volume and complexity of data. To overcome these challenges, consider using software tools specifically designed for qualitative analysis, such as NVivo or ATLAS.ti. These tools can help you organize and code your data efficiently. Additionally, developing a clear coding framework and regularly discussing and refining your codes with colleagues can enhance the quality of your analysis.
How can I present my qualitative research findings effectively to a non-academic audience?
+
When presenting your findings to a non-academic audience, it’s important to simplify and translate your research into accessible language. Use clear and concise language, avoid excessive jargon, and focus on the key insights and implications of your research. Visual aids, such as infographics or charts, can also help convey complex information in a more engaging and understandable manner.
What are some best practices for conducting qualitative interviews?

+
When conducting qualitative interviews, it’s crucial to create a comfortable and safe environment for participants. Use open-ended questions to encourage in-depth responses and allow for exploration of unexpected themes. Be an active listener, show empathy, and maintain a non-judgmental attitude. Additionally, consider using a semi-structured interview guide to ensure consistency while allowing for flexibility and exploration of emerging topics.