Qualitative data analysis is a powerful process that involves examining and interpreting non-numerical information to uncover patterns, themes, and insights. It plays a crucial role in various fields, including social sciences, market research, and healthcare, by providing a deeper understanding of human behavior, experiences, and attitudes. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of qualitative data analysis, exploring its importance, techniques, and the steps involved in conducting a comprehensive analysis.
Understanding Qualitative Data
Qualitative data refers to descriptive information that cannot be measured quantitatively. It captures the richness and complexity of human experiences, beliefs, and opinions. Common sources of qualitative data include interviews, focus groups, observations, documents, and open-ended survey responses. Unlike quantitative data, which relies on numerical values and statistical analysis, qualitative data analysis focuses on the meaning and context behind the information.
The Importance of Qualitative Data Analysis

Qualitative data analysis offers a unique perspective that complements quantitative research. Here are some key reasons why qualitative data analysis is essential:
- Uncovering Hidden Insights: Qualitative analysis allows researchers to explore complex and nuanced aspects of a topic that may not be captured by quantitative methods alone.
- Understanding Context: It provides a deeper understanding of the context in which data is generated, helping to interpret findings accurately.
- Exploring Subjective Experiences: Qualitative data analysis is particularly valuable when studying human experiences, emotions, and perceptions, which are often subjective and difficult to quantify.
- Identifying Patterns and Themes: By analyzing qualitative data, researchers can identify recurring patterns, themes, and trends that emerge from the data.
- Informing Decision-Making: The insights gained from qualitative analysis can guide decision-making processes, policy development, and the design of interventions or strategies.
Techniques for Qualitative Data Analysis

There are several techniques and approaches used in qualitative data analysis. Here are some commonly employed methods:
Content Analysis

Content analysis involves systematically analyzing and interpreting textual data, such as transcripts, documents, or social media posts. It focuses on identifying patterns, themes, and trends within the content. Researchers often use coding, which involves assigning labels or codes to segments of text to categorize and organize the data.
Thematic Analysis

Thematic analysis is a widely used approach that aims to identify and analyze patterns or themes within qualitative data. It involves a systematic process of coding, categorizing, and interpreting data to develop a comprehensive understanding of the research topic. Thematic analysis is flexible and can be applied to various types of qualitative data, including interviews, focus groups, and observational notes.
Grounded Theory

Grounded theory is a research methodology that aims to develop theories based on systematic analysis of qualitative data. It involves an iterative process of data collection and analysis, where theories are generated and refined as new data is collected. Grounded theory emphasizes the importance of data-driven theory development, allowing researchers to uncover patterns and relationships within the data.
Narrative Analysis
Narrative analysis focuses on analyzing and interpreting personal stories or narratives. It explores how individuals construct and communicate their experiences, beliefs, and identities through storytelling. Narrative analysis can provide insights into cultural norms, social practices, and the ways individuals make sense of their world.
Discourse Analysis

Discourse analysis examines the use of language and communication in social contexts. It involves analyzing the structure, content, and function of discourse to understand how language shapes and reflects social realities. Discourse analysis can be applied to various forms of communication, including written texts, speeches, and online interactions.
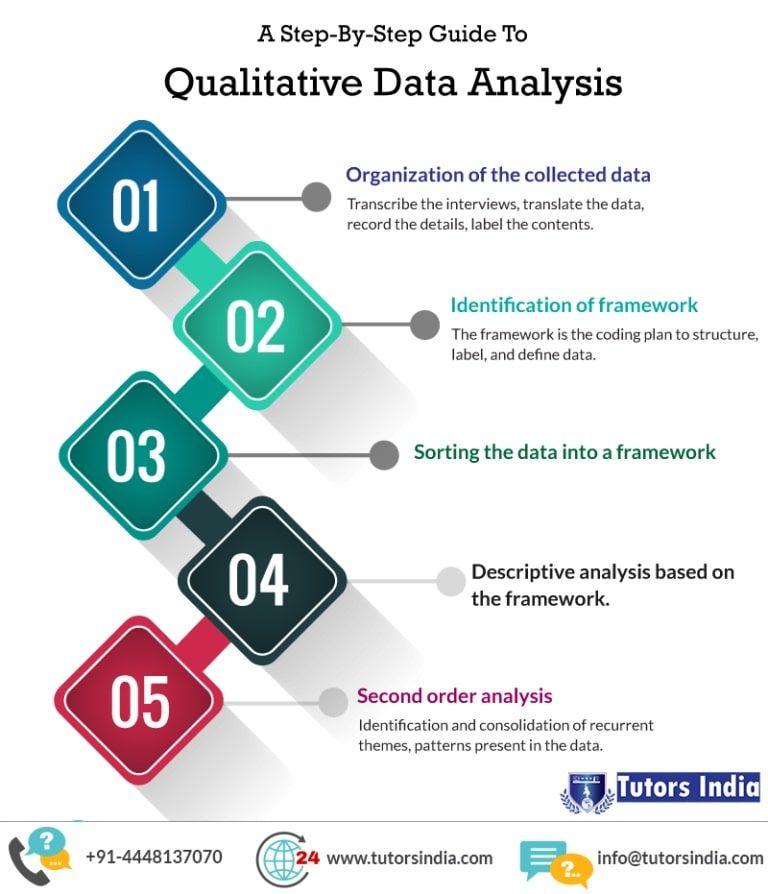
Steps in Qualitative Data Analysis

Conducting a comprehensive qualitative data analysis involves several steps. Here is a general overview of the process:
-
Data Collection

The first step is to collect qualitative data through various methods such as interviews, focus groups, observations, or document analysis. It is essential to ensure that the data collection process is systematic and aligns with the research objectives.
-
Transcription and Preparation

If the data collection involves audio or video recordings, transcription is necessary. Transcripts should be carefully prepared, ensuring accuracy and clarity. Additionally, any relevant documents or observational notes should be organized and prepared for analysis.
-
Familiarization with Data

Researchers should immerse themselves in the data by reading through transcripts, documents, or observational notes multiple times. This step allows researchers to become familiar with the data, identify initial patterns or themes, and develop a deeper understanding of the context.
-
Coding

Coding is a crucial step in qualitative data analysis. It involves assigning labels or codes to segments of data to categorize and organize the information. Codes can be generated inductively (based on the data) or deductively (based on existing theories or research questions). Coding helps to identify patterns, themes, and relationships within the data.
-
Theme Development

Based on the codes generated during the coding process, researchers can identify and develop themes. Themes represent recurring patterns or ideas that emerge from the data. It is important to review and refine themes to ensure they accurately reflect the data and research objectives.
-
Analysis and Interpretation
Once themes are identified, researchers can analyze and interpret the data within each theme. This involves exploring the relationships between themes, identifying sub-themes, and developing a comprehensive understanding of the research topic. Interpretation should be supported by evidence from the data and linked to the research questions or objectives.
-
Writing and Reporting
The final step is to write and report the findings of the qualitative data analysis. This involves organizing and presenting the results in a clear and concise manner. Researchers should provide a detailed description of the analysis process, including the methods used, the coding framework, and the themes identified. It is essential to support the findings with relevant quotes or examples from the data to enhance credibility and transparency.
Challenges and Considerations

Qualitative data analysis presents several challenges and considerations that researchers should be aware of:
- Subjectivity: Qualitative analysis is inherently subjective, as it involves interpreting and making sense of data based on the researcher's perspective. Researchers should aim for transparency and reflexivity to acknowledge and minimize the impact of their biases.
- Time and Resource Intensive: Conducting a rigorous qualitative data analysis requires significant time and resources. Researchers should plan and allocate sufficient time for data collection, transcription, analysis, and writing.
- Ethical Considerations: Qualitative research often involves collecting sensitive and personal information. Researchers must ensure the anonymity and confidentiality of participants and obtain informed consent. Ethical guidelines and institutional review board approvals should be followed.
- Generalizability: Qualitative research typically focuses on specific contexts or populations. The findings may not be generalizable to other contexts or populations. Researchers should be cautious when drawing broader conclusions and consider the transferability of the findings.
Conclusion

Qualitative data analysis is a powerful tool for gaining insights into complex human experiences, beliefs, and attitudes. By employing various techniques such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and discourse analysis, researchers can uncover hidden patterns, develop theories, and inform decision-making processes. While qualitative analysis presents challenges, such as subjectivity and time intensity, it offers a unique perspective that complements quantitative research. By following a systematic approach and considering ethical guidelines, researchers can conduct rigorous qualitative data analysis and contribute to a deeper understanding of the research topic.
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data analysis?
+Qualitative data analysis focuses on interpreting non-numerical information, such as interviews and observations, to uncover patterns and themes. Quantitative data analysis, on the other hand, involves analyzing numerical data using statistical methods to identify relationships and make predictions.
How can I ensure the reliability of qualitative data analysis?
+To ensure reliability, it is important to follow a systematic and rigorous approach. This includes clearly defining research objectives, using appropriate sampling techniques, and employing multiple coders or analysts to enhance inter-rater reliability. Additionally, maintaining detailed documentation and providing clear justification for coding decisions can enhance the reliability of the analysis.
What are some common challenges in qualitative data analysis?
+Challenges in qualitative data analysis include managing large amounts of data, ensuring consistency in coding and analysis, and addressing researcher bias. It is crucial to have a well-defined coding framework, regular coding meetings to discuss discrepancies, and a reflective approach to minimize the impact of personal biases.
How can qualitative data analysis benefit businesses or organizations?
+Qualitative data analysis provides valuable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and experiences. By understanding the perspectives and needs of their target audience, businesses can make informed decisions regarding product development, marketing strategies, and customer service improvements. It helps organizations gain a competitive edge and enhance their overall performance.
Are there any software tools available for qualitative data analysis?
+Yes, there are several software tools specifically designed for qualitative data analysis. These tools, such as NVivo, ATLAS.ti, and MAXQDA, offer features like coding, theme development, and data visualization. They can streamline the analysis process, enhance collaboration, and facilitate the management of large datasets.