Geospatial data, often referred to as geospatial information or simply geodata, is a powerful tool that has revolutionized how we understand and interact with our world. It combines geographical locations with various types of data, providing valuable insights and enabling us to make informed decisions across numerous fields.
In this blog post, we will delve into the world of geospatial data, exploring its definition, types, applications, and the impact it has on our daily lives. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of this fascinating field and its endless possibilities.
Understanding Geospatial Data
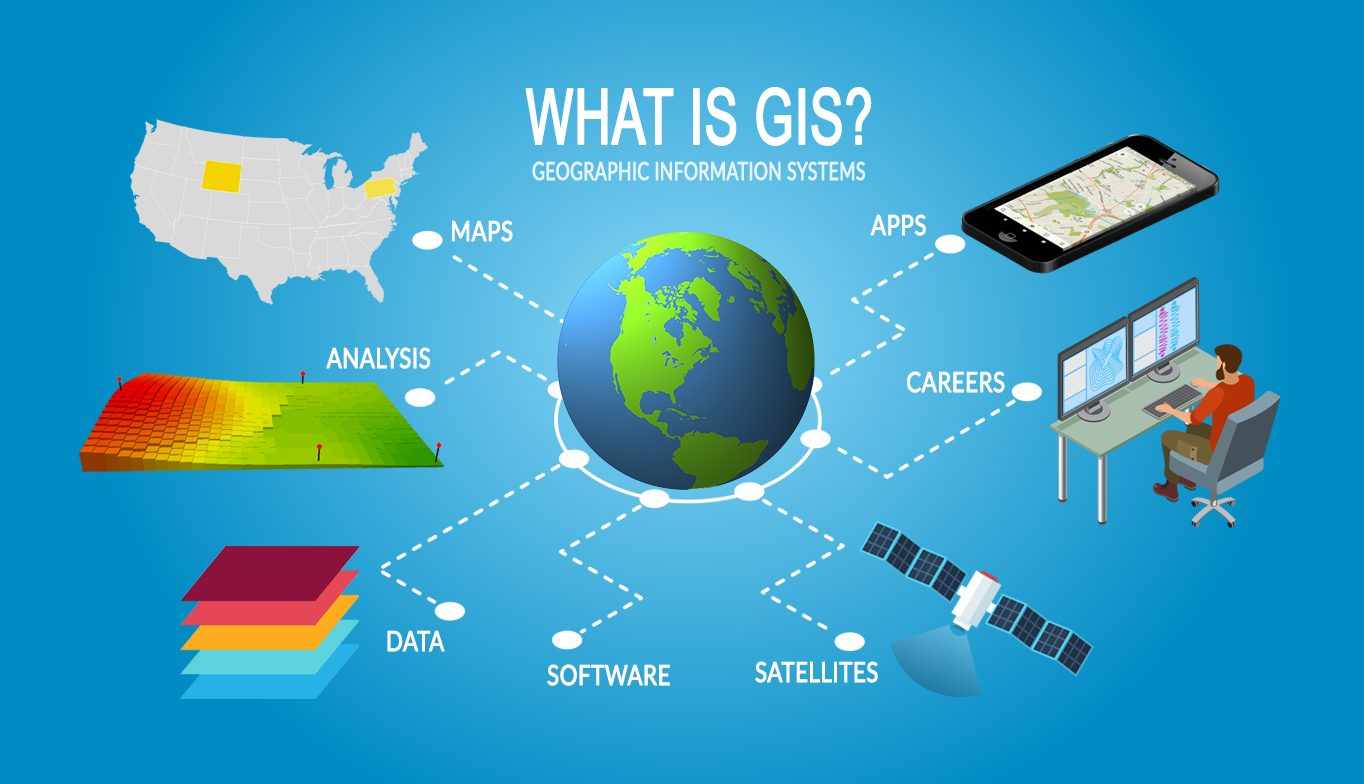
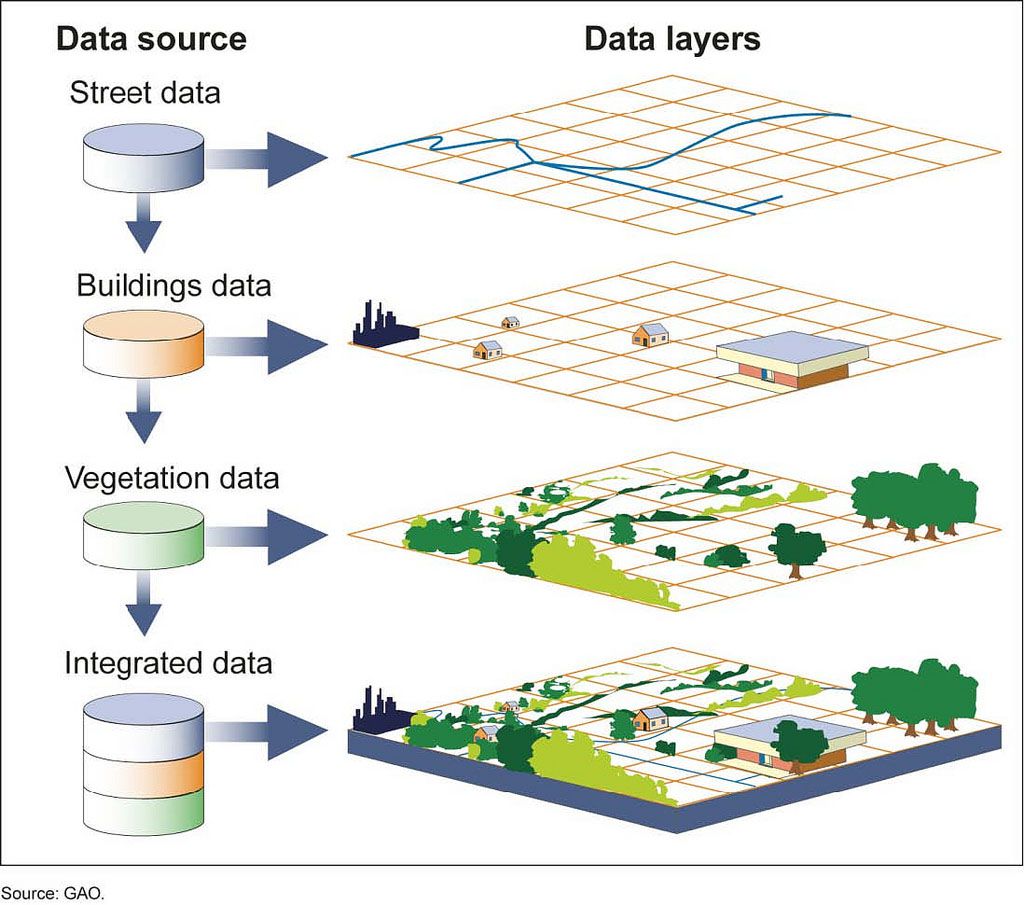
Geospatial data is a collection of information that describes the physical or geographical features of our planet. It goes beyond simple location coordinates by incorporating additional attributes and characteristics associated with specific places.
Key Characteristics of Geospatial Data
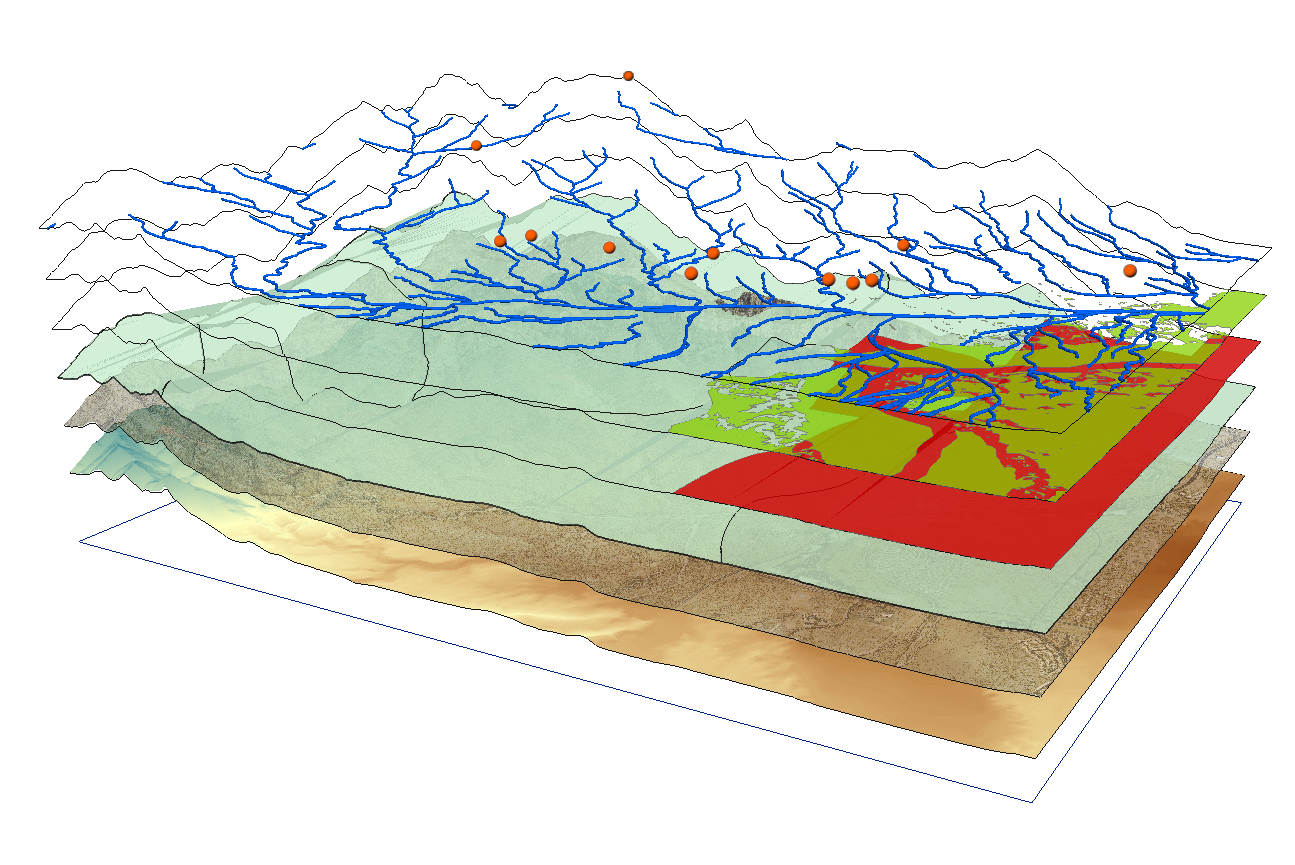
- Location: At its core, geospatial data is anchored to a specific location on Earth, whether it's a point, line, or polygon.
- Attributes: Beyond coordinates, geospatial data includes various attributes such as elevation, land cover, population density, and more.
- Spatial Relationships: Geospatial data considers the relationships between different locations, allowing for analysis and visualization of patterns and trends.
Types of Geospatial Data

Geospatial data comes in various forms, each serving unique purposes. Here are some common types:
Vector Data
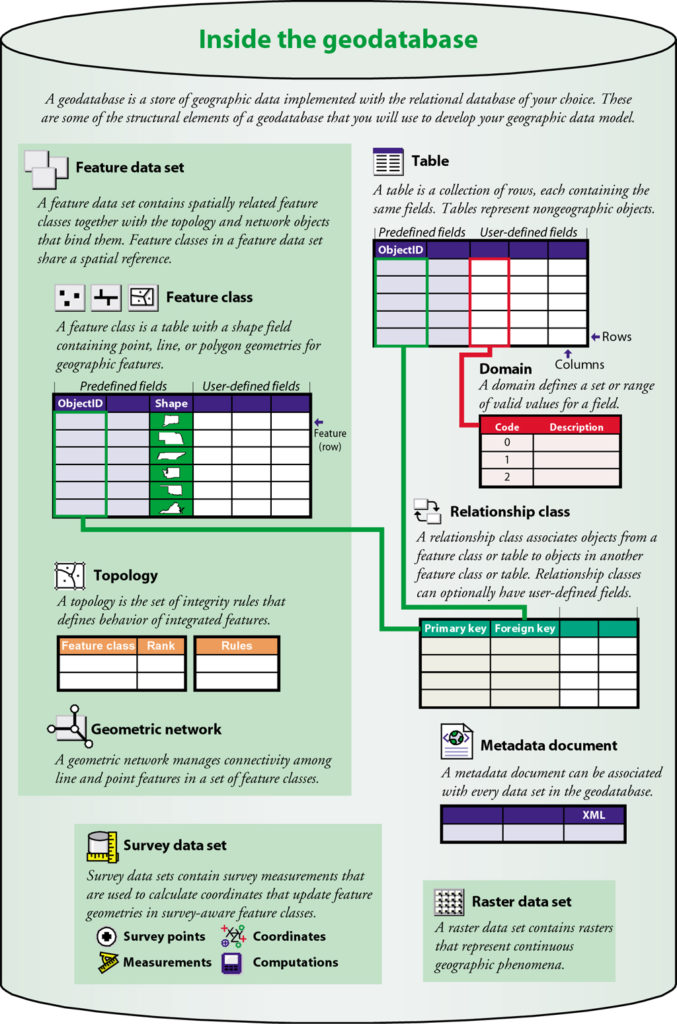
Vector data represents geographic features as points, lines, or polygons. It is highly accurate and commonly used for mapping and GIS (Geographic Information System) applications.
Raster Data
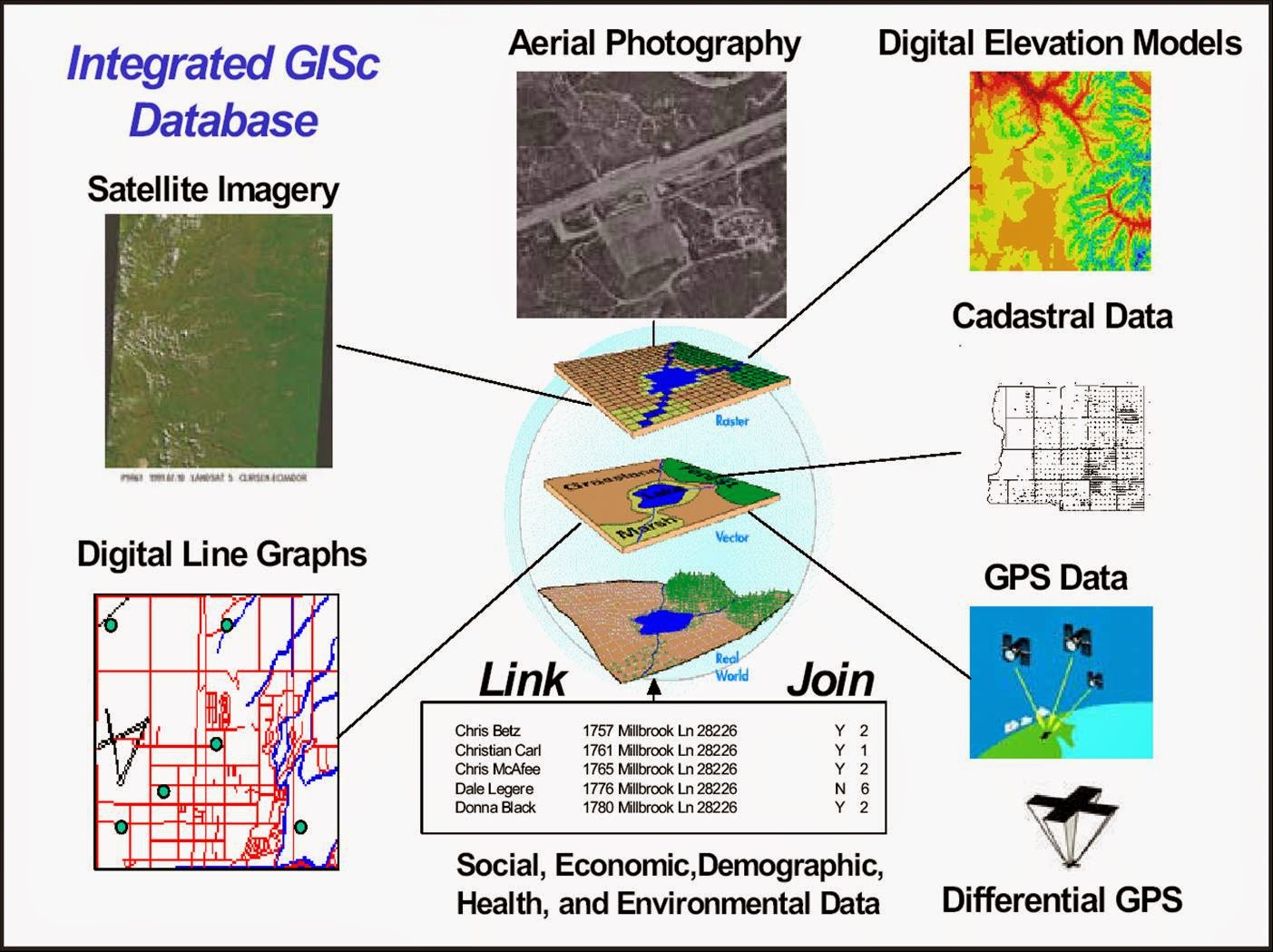
Raster data, on the other hand, consists of grids of cells, with each cell containing a value. It is widely used for satellite imagery, digital elevation models, and remote sensing applications.
Topographic Data

Topographic data provides detailed information about the physical features of an area, including elevation, contour lines, and landforms. It is crucial for understanding terrain and planning infrastructure projects.
Remote Sensing Data

Remote sensing data is obtained through sensors and cameras on satellites or aircraft. It captures information about the Earth's surface, atmosphere, and oceans, enabling us to monitor changes and study environmental patterns.
Applications of Geospatial Data

The applications of geospatial data are vast and diverse, impacting numerous industries and sectors. Here are some key areas where geospatial data plays a crucial role:
Urban Planning and Development
- Geospatial data helps urban planners make informed decisions about land use, transportation networks, and infrastructure development.
- It enables the identification of suitable locations for new developments, taking into account factors like population density, environmental impact, and accessibility.
Environmental Monitoring and Conservation

- Geospatial data is vital for monitoring and studying the Earth's environment, including climate change, deforestation, and natural disasters.
- It assists in identifying vulnerable ecosystems, tracking wildlife populations, and implementing conservation efforts.
Natural Resource Management
- Geospatial data aids in the sustainable management of natural resources such as water, minerals, and forests.
- It helps optimize resource extraction, monitor resource depletion, and ensure responsible practices.
Emergency Response and Disaster Management

- During emergencies and natural disasters, geospatial data becomes a critical tool for emergency responders.
- It provides real-time information on affected areas, helps coordinate rescue efforts, and aids in post-disaster recovery planning.
Transportation and Logistics

- Geospatial data optimizes transportation routes, improves traffic management, and enhances logistics operations.
- It enables the development of intelligent transportation systems and supports the efficient movement of goods and people.
Agriculture and Food Security
- Geospatial data assists farmers in making data-driven decisions, such as crop selection, irrigation management, and pest control.
- It contributes to increasing agricultural productivity and ensuring food security on a global scale.
Tools and Technologies

Several tools and technologies are used to collect, analyze, and visualize geospatial data. Here are some key ones:
Global Positioning System (GPS)
GPS technology provides accurate location information, allowing for precise mapping and data collection.
Remote Sensing Satellites
Satellites equipped with remote sensing technology capture high-resolution imagery and data, offering a comprehensive view of the Earth's surface.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
GIS software integrates and analyzes geospatial data, enabling users to create maps, perform spatial analysis, and make informed decisions.
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
LiDAR uses laser technology to create detailed 3D models of the Earth's surface, providing accurate elevation data and terrain mapping.
Challenges and Considerations

While geospatial data offers immense benefits, there are challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
Data Accuracy and Quality
Ensuring the accuracy and quality of geospatial data is crucial. Inaccurate or outdated data can lead to incorrect analysis and decision-making.
Data Privacy and Security
Geospatial data often contains sensitive information, and protecting user privacy and data security is essential.
Data Sharing and Collaboration
Effective data sharing and collaboration among organizations and stakeholders are necessary to maximize the benefits of geospatial data.
The Future of Geospatial Data

The field of geospatial data is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand for location-based information. Here are some trends to watch out for:
Big Data and Geospatial Analytics
The integration of geospatial data with big data analytics opens up new possibilities for advanced spatial analysis and decision-making.
Internet of Things (IoT) and Geospatial Integration
The IoT revolution is expected to generate vast amounts of geospatial data, leading to new applications and insights.
Machine Learning and AI
Machine learning algorithms can enhance geospatial data analysis, enabling automated pattern recognition and prediction.
3D Mapping and Virtual Reality
Advancements in 3D mapping and virtual reality technologies will provide immersive experiences, allowing users to explore and interact with geospatial data in new ways.
Conclusion

Geospatial data has become an indispensable tool, shaping the way we understand and interact with our planet. Its applications are far-reaching, impacting fields such as urban planning, environmental conservation, and emergency response. As technology continues to advance, the potential for geospatial data to revolutionize our world is limitless. By embracing its power and addressing the associated challenges, we can unlock new opportunities and create a more sustainable and efficient future.
What is the difference between vector and raster data?
+Vector data represents geographic features as points, lines, or polygons, offering high accuracy and precision. Raster data, on the other hand, consists of grids of cells, with each cell containing a value. It is commonly used for satellite imagery and remote sensing applications.
How is geospatial data collected?
+Geospatial data is collected through various methods, including GPS technology, remote sensing satellites, aerial surveys, and ground-based measurements. These tools capture location information and attributes, which are then processed and analyzed.
What are some common applications of geospatial data in everyday life?
+Geospatial data is used in various everyday applications, such as navigation systems, weather forecasting, real estate analysis, and location-based services. It helps us make informed decisions and navigate our surroundings efficiently.
How can geospatial data contribute to environmental conservation efforts?
+Geospatial data plays a crucial role in environmental conservation by providing insights into ecosystem health, wildlife behavior, and habitat monitoring. It assists in identifying areas of concern, tracking changes over time, and supporting conservation planning.
What are the key benefits of using geospatial data in urban planning?
+Geospatial data enables urban planners to make data-driven decisions, optimize land use, and improve the overall livability of cities. It helps identify suitable locations for infrastructure, analyze population patterns, and enhance transportation networks.