Geospatial software has become an essential tool for businesses and organizations across various industries, offering powerful capabilities for data analysis, visualization, and decision-making. From mapping and navigation to spatial data management and advanced geospatial analytics, this software empowers users to uncover valuable insights and make informed choices. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the world of geospatial software, covering its key features, applications, and benefits. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced user, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and tools to master geospatial software and unlock its full potential.
Understanding Geospatial Software

Geospatial software, also known as geographic information system (GIS) software, is a powerful tool that enables users to collect, manage, analyze, and visualize spatial data. It integrates geographical features with tabular data, allowing for a deeper understanding of relationships and patterns within a geographic context. By leveraging geospatial software, organizations can make data-driven decisions, optimize processes, and gain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
Key Features of Geospatial Software
- Data Management: Geospatial software provides a robust platform for storing, organizing, and managing spatial data. It supports various data formats, including shapefiles, geodatabases, and raster images, allowing users to efficiently handle large volumes of geographical information.
- Data Analysis: One of the primary strengths of geospatial software is its analytical capabilities. It offers a wide range of tools for spatial analysis, such as spatial statistics, geoprocessing, and spatial queries. These features enable users to derive meaningful insights from spatial data, identify patterns, and make informed decisions.
- Visualization and Mapping: Geospatial software excels in creating visually appealing maps and spatial representations. It offers a variety of map styles, symbology options, and customization features, allowing users to present data in a clear and intuitive manner. Interactive maps and 3D visualizations further enhance the user experience and facilitate data exploration.
- Geocoding and Address Matching: Geospatial software simplifies the process of converting addresses into geographic coordinates (geocoding) and matching locations to their corresponding addresses. This feature is crucial for applications like location-based services, market analysis, and emergency response planning.
- Spatial Data Editing and Digitizing: Users can create and edit spatial data directly within geospatial software. This includes tools for digitizing features from maps, creating new shapes, and modifying existing geometries. The ability to edit and manipulate spatial data is essential for maintaining accurate and up-to-date datasets.
- Geospatial Web Services: Many geospatial software solutions offer web services and APIs, enabling the integration of spatial data into web applications and services. This allows for the development of interactive maps, location-based services, and geospatial data sharing across platforms.
Applications of Geospatial Software
Geospatial software finds applications in a wide range of industries and domains. Here are some key areas where geospatial software plays a vital role:
- Urban Planning and Development: Geospatial software assists urban planners and developers in analyzing demographic data, land use patterns, and infrastructure networks. It helps in making informed decisions about land development, zoning, and transportation planning.
- Environmental Monitoring and Management: Environmental agencies and researchers use geospatial software to monitor and manage natural resources, track environmental changes, and assess the impact of human activities. It aids in conservation efforts, disaster management, and sustainable development planning.
- Transportation and Logistics: Geospatial software is instrumental in optimizing transportation networks, routing, and fleet management. It helps businesses and organizations plan efficient routes, analyze traffic patterns, and improve overall logistics operations.
- Telecommunications and Network Planning: Telecommunications companies rely on geospatial software to plan and optimize their network infrastructure. It assists in site selection, coverage analysis, and network capacity planning, ensuring efficient and reliable communication services.
- Public Safety and Emergency Response: Geospatial software plays a critical role in emergency management, providing real-time spatial data and analytics. It aids in disaster response, incident mapping, and resource allocation, helping emergency responders make critical decisions during critical situations.
- Market Analysis and Location Intelligence: Businesses use geospatial software to analyze market trends, customer demographics, and competitor locations. It helps in making strategic decisions about store locations, targeted marketing campaigns, and understanding customer behavior patterns.
Benefits of Geospatial Software

Implementing geospatial software offers numerous benefits to organizations and businesses:
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Geospatial software provides a comprehensive view of spatial data, enabling users to make informed decisions based on accurate and up-to-date information. It helps identify trends, patterns, and correlations that may not be apparent through traditional data analysis methods.
- Efficient Data Management: With its robust data management capabilities, geospatial software allows organizations to centralize and organize spatial data. This streamlines data access, sharing, and collaboration, ensuring that the right information is available to the right people at the right time.
- Enhanced Visualization and Communication: Geospatial software's visualization capabilities transform complex spatial data into intuitive and visually appealing maps and charts. This facilitates better communication and understanding of spatial information, making it easier to convey insights and ideas to stakeholders and decision-makers.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: By leveraging geospatial software, organizations can optimize their operations and processes. It enables better planning, resource allocation, and decision-making, leading to increased efficiency, cost savings, and improved overall performance.
- Spatial Data Integration: Geospatial software integrates seamlessly with other data sources and systems, allowing organizations to combine spatial data with other relevant information. This integration enhances the value of data and enables more comprehensive analysis and decision-making.
Getting Started with Geospatial Software

If you're new to geospatial software, here are some steps to help you get started:
- Choose the Right Software: Select a geospatial software solution that aligns with your specific needs and requirements. Consider factors such as the type of data you work with, the scale of your projects, and the level of complexity you require.
- Familiarize Yourself with the Interface: Take the time to explore the software's interface and understand its basic functionality. Most geospatial software providers offer tutorials, documentation, and online resources to help you get familiar with the tools and features.
- Start with Simple Projects: Begin with small-scale projects to gain hands-on experience. Work with basic data sets and explore the software's capabilities. As you become more comfortable, gradually increase the complexity of your projects.
- Utilize Online Resources: There is a wealth of online resources available, including tutorials, video guides, and community forums. These resources can provide valuable insights and help you overcome common challenges when working with geospatial software.
- Join User Communities: Engage with the geospatial software user community. Participate in online forums, attend webinars, and connect with experts and fellow users. Sharing experiences and knowledge can greatly enhance your understanding and proficiency with the software.
Tips for Effective Geospatial Software Usage

To make the most of your geospatial software experience, consider the following tips:
- Organize Your Data: Maintain a well-organized data structure and naming conventions. This will make it easier to locate and manage your spatial data, especially when working with large datasets.
- Explore Advanced Features: Geospatial software offers a wide range of advanced features and tools. Take the time to explore and experiment with these features to unlock the full potential of the software and enhance your analysis capabilities.
- Collaborate and Share: Geospatial software often supports collaboration and data sharing. Utilize these features to work effectively with team members and stakeholders, ensuring everyone has access to the latest spatial data and insights.
- Stay Updated: Keep yourself informed about the latest updates and advancements in geospatial software. Attend industry events, conferences, and webinars to stay abreast of new features, best practices, and emerging trends.
Advanced Geospatial Software Concepts
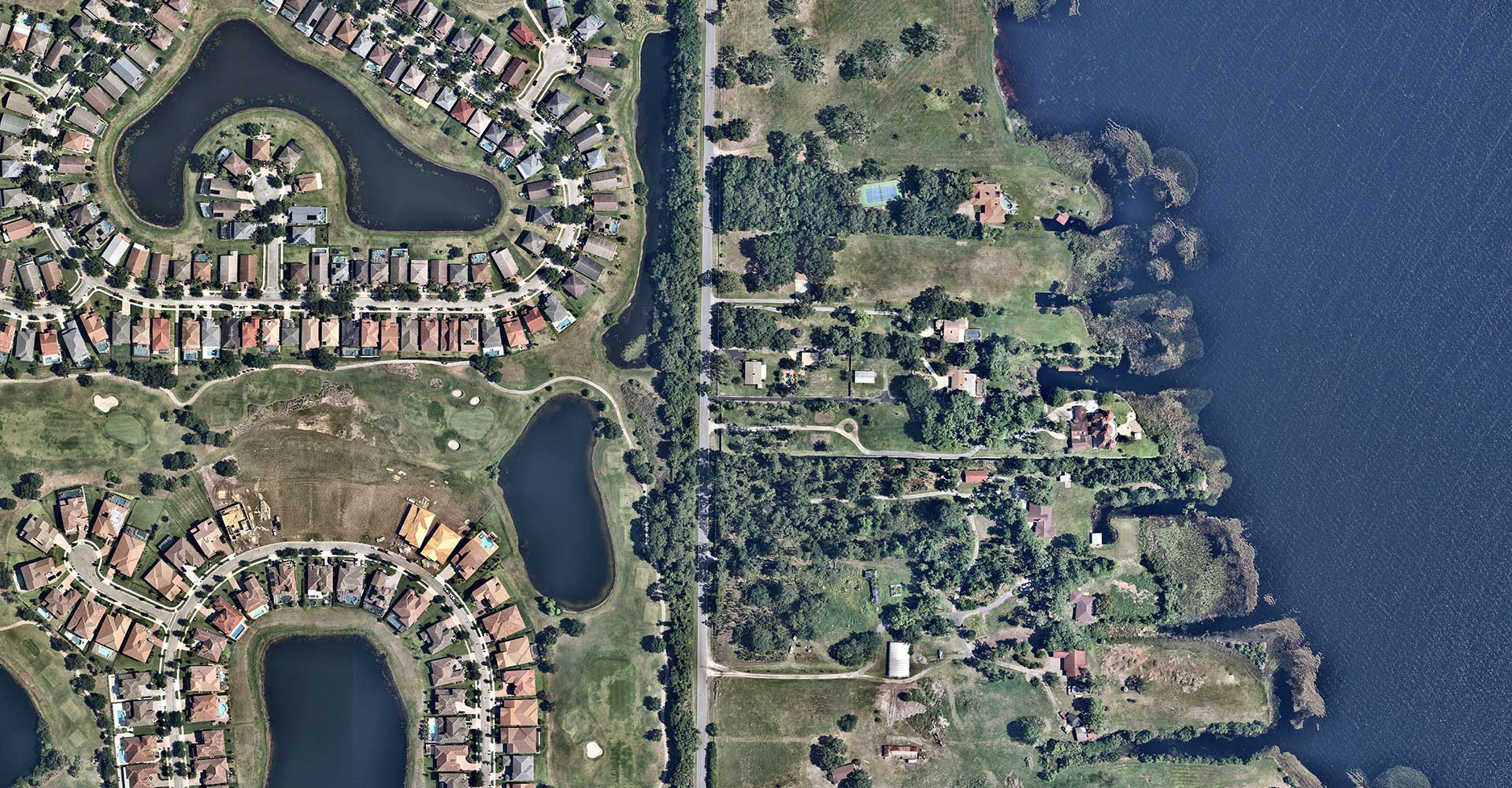

As you become more proficient with geospatial software, you may want to explore advanced concepts and techniques. Here are some key areas to delve into:
- Spatial Statistics: Spatial statistics involve analyzing spatial data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships. This includes techniques such as spatial autocorrelation, spatial regression, and spatial clustering, which provide valuable insights for decision-making.
- Geospatial Modeling: Geospatial modeling involves creating and simulating real-world scenarios using spatial data. It allows for the analysis of complex systems, such as urban growth, environmental impacts, and transportation networks, and helps in predicting future outcomes.
- Spatial Data Fusion: Spatial data fusion combines multiple spatial datasets to create more comprehensive and accurate representations. This technique is particularly useful when dealing with diverse data sources and requires careful data integration and processing.
- Remote Sensing and Image Analysis: Geospatial software often integrates with remote sensing technologies, allowing for the analysis of satellite and aerial imagery. This enables the extraction of valuable information from images, such as land cover classification, change detection, and object recognition.
- 3D Visualization and Analysis: Three-dimensional (3D) visualization and analysis provide a more immersive and realistic representation of spatial data. It enables users to explore complex spatial relationships, perform advanced analysis, and communicate findings effectively.
Conclusion
Geospatial software has revolutionized the way we understand and interact with spatial data. Its powerful features, from data management to advanced analysis, enable organizations to make informed decisions, optimize processes, and gain a competitive advantage. By mastering geospatial software, you can unlock a world of possibilities and become a spatial data expert. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced user, the key is to explore, learn, and apply these tools to solve real-world challenges and drive innovation.
What is the purpose of geospatial software?

+
Geospatial software is designed to collect, manage, analyze, and visualize spatial data. It helps organizations make data-driven decisions, optimize processes, and gain a competitive edge by providing insights into geographic relationships and patterns.
What industries benefit from geospatial software?
+
Geospatial software finds applications in various industries, including urban planning, environmental management, transportation, telecommunications, public safety, and market analysis. Its versatility makes it valuable for organizations across different sectors.
How can I choose the right geospatial software for my needs?

+
When selecting geospatial software, consider factors such as your data requirements, project scale, and desired level of complexity. Evaluate the software’s features, compatibility with your existing systems, and the level of support and resources provided by the software vendor.
What are some common challenges when working with geospatial software?
+
Common challenges include managing large spatial datasets, ensuring data accuracy and quality, and learning the software’s interface and tools. However, with proper training, resources, and a systematic approach, these challenges can be overcome.
How can I stay updated with the latest advancements in geospatial software?

+
Staying updated with geospatial software advancements involves attending industry events, conferences, and webinars. Subscribing to relevant newsletters, blogs, and online communities can also provide valuable insights and keep you informed about the latest trends and developments.