Calculating the area under a curve is a common task in data analysis, and Excel provides several methods to achieve this. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore six different ways to calculate the area under a curve using Excel, along with practical examples and step-by-step instructions. By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of these techniques and be able to choose the most suitable method for your specific needs.
Method 1: Using the Trapz Function
The Trapz function is a built-in Excel formula that calculates the approximate area under a curve using the trapezoidal rule. It is a simple and effective method for estimating areas, especially when dealing with evenly spaced data points.
Step-by-Step Guide

- Organize your data in Excel. Ensure that your x-values are in one column and the corresponding y-values are in another column.
- In an empty cell, enter the formula:
=TRAPZ(y_values, x_values), wherey_valuesis the range of y-values andx_valuesis the range of x-values. - Press Enter to calculate the area under the curve.
Example

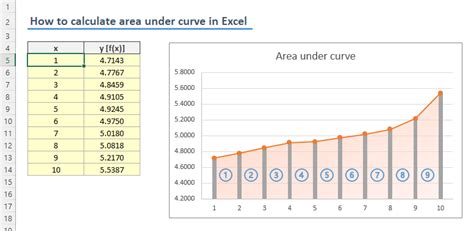
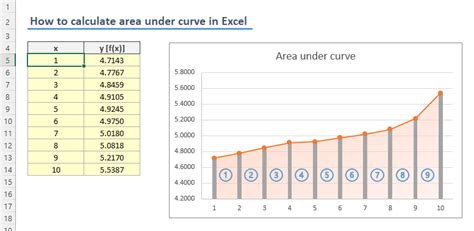
Suppose we have the following data:
| X | Y |
|---|---|
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 6 |
| 4 | 8 |

To calculate the area under the curve, we can use the formula: =TRAPZ(B2:B5, A2:A5) where B2:B5 represents the y-values and A2:A5 represents the x-values.
Method 2: The Integral Function
Excel's Integral function calculates the definite integral of a function over a specified interval. It is particularly useful when you have a formula that defines the curve.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Define your curve using a formula in Excel. For example, you can use the formula
=A2^2to represent a quadratic curve. - In an empty cell, enter the formula:
=INTEGRAL(formula, x_start, x_end), whereformulais the cell reference or formula representing the curve,x_startis the starting x-value, andx_endis the ending x-value. - Press Enter to obtain the area under the curve.
Example

Consider the quadratic curve defined by the formula =A2^2. To calculate the area under the curve from x = 1 to x = 4, use the formula: =INTEGRAL(A2^2, 1, 4).
Method 3: Riemann Sum Approximation
The Riemann sum approximation method divides the area under the curve into rectangles and calculates their areas to approximate the total area. This method is flexible and can handle various types of curves.
Step-by-Step Guide

- Arrange your data in Excel with x-values in one column and y-values in another.
- In an empty cell, enter the formula:
=SUM(y_values) * (x_values[last] - x_values[first]), wherey_valuesis the range of y-values andx_values[last]andx_values[first]are the last and first x-values, respectively. - Press Enter to get the approximate area under the curve.
Example
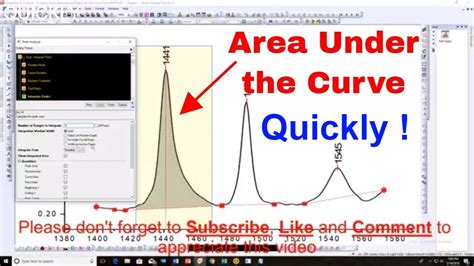
Given the data from the previous example, we can calculate the approximate area under the curve using the formula: =SUM(B2:B5) * (A5 - A2).
Method 4: Area Function for Continuous Functions

Excel's Area function calculates the area under a curve defined by a continuous function. It is a powerful tool for analyzing continuous data sets.
Step-by-Step Guide

- Define your curve using a formula in Excel. For instance, you can use
=SIN(A2)to represent a sine curve. - In an empty cell, enter the formula:
=AREA(formula, x_start, x_end), whereformulais the cell reference or formula representing the curve, andx_startandx_endare the starting and ending x-values, respectively. - Press Enter to calculate the area under the curve.
Example

To find the area under the sine curve from x = 0 to x = 2π, use the formula: =AREA(SIN(A2), 0, 2*PI()).
Method 5: Area Function for Discrete Data
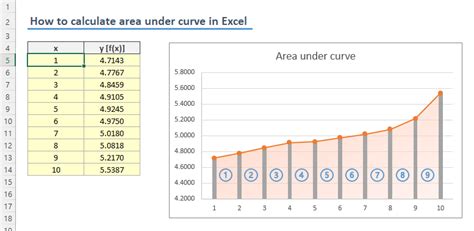
The Area function can also be used for discrete data sets. It calculates the area under a curve defined by a discrete set of points.
Step-by-Step Guide

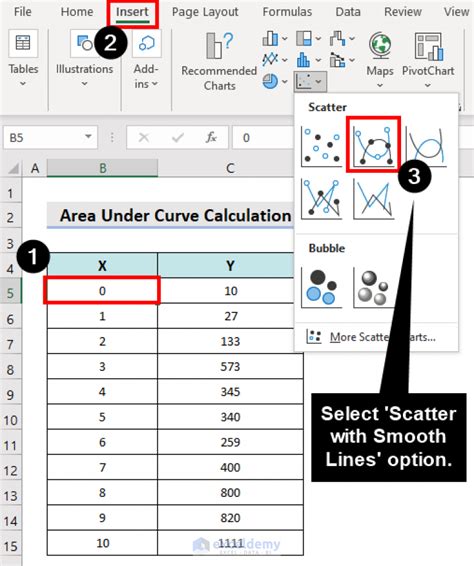
- Arrange your discrete data in Excel with x-values in one column and y-values in another.
- In an empty cell, enter the formula:
=AREA(y_values, x_values), wherey_valuesis the range of y-values andx_valuesis the range of x-values. - Press Enter to obtain the area under the curve.
Example

For the data provided earlier, you can calculate the area under the curve using the formula: =AREA(B2:B5, A2:A5).
Method 6: Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) Code

If you have advanced knowledge of VBA, you can create a custom function to calculate the area under a curve. This method offers flexibility and control over the calculation process.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Open the Visual Basic Editor by pressing
Alt + F11in Excel. - Insert a new module and paste the following VBA code:
Function AreaUnderCurve(xValues As Range, yValues As Range) As Double
Dim i As Long
Dim n As Long
Dim dx As Double
Dim integral As Double
n = xValues.Count
dx = (xValues(n, 1) - xValues(1, 1)) / (n - 1)
For i = 1 To n - 1
integral = integral + (yValues(i, 1) + yValues(i + 1, 1)) * dx / 2
Next i
AreaUnderCurve = integral
End Function
- Save the module and close the Visual Basic Editor.
- In an empty cell, enter the formula:
=AreaUnderCurve(x_values, y_values), wherex_valuesandy_valuesare the ranges of x and y values, respectively. - Press Enter to calculate the area under the curve.
Example
For the data in our example, use the formula: =AreaUnderCurve(A2:A5, B2:B5) to calculate the area under the curve.
Conclusion
Excel provides a range of methods to calculate the area under a curve, each with its own advantages and use cases. Whether you prefer built-in functions like Trapz, Integral, and Area, or more advanced techniques like Riemann sum approximation or VBA coding, you now have the tools to tackle various curve-related calculations. Choose the method that best suits your data and requirements, and let Excel assist you in uncovering valuable insights from your data.
FAQ
Can I use Excel to calculate the area under a curve for complex functions?
+Yes, Excel’s Integral and Area functions are capable of handling complex functions. You can define the curve using a formula and specify the integration interval to calculate the area accurately.
Is there a way to calculate the area under a curve for irregular data points in Excel?
+Yes, you can use the Trapz function to calculate the area under a curve for irregularly spaced data points. Excel will automatically adjust the trapezoidal rule to accommodate the uneven spacing.
Can I calculate the area under a curve in Excel without knowing the exact formula?
+Yes, if you have discrete data points, you can use the Area function to calculate the area under the curve. This method is suitable for data sets with discrete x and y values.
How accurate are the area calculations using Excel’s built-in functions?
+Excel’s built-in functions, such as Trapz, Integral, and Area, provide accurate results for most use cases. However, for highly complex or irregular curves, more advanced mathematical software might be necessary for precise calculations.