In today's digital age, where information is readily available at our fingertips, it's crucial to understand the distinction between disinformation and misinformation. These two terms, often used interchangeably, refer to different types of false or misleading information that can have significant impacts on our society and individual lives. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of disinformation and misinformation, exploring their definitions, impacts, and how to identify and combat them.
Understanding Disinformation and Misinformation

Disinformation and misinformation are two concepts that have gained prominence in recent years, especially with the rise of social media and the ease of information sharing. While they may seem similar, they have distinct characteristics and implications.
Misinformation

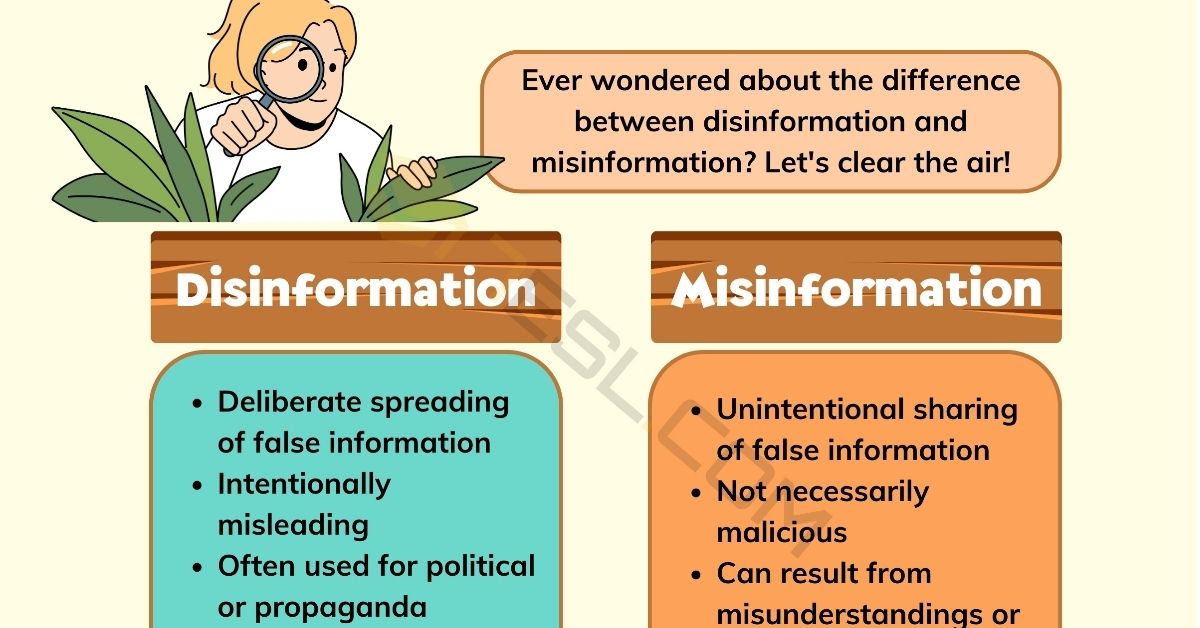
Misinformation refers to false or inaccurate information that is unintentionally shared. It is often a result of human error, misinterpretation, or the spread of outdated information. People who share misinformation usually do so without the intention to deceive or cause harm. Misinformation can be as simple as a rumor or a misconception that spreads through word of mouth or online platforms.
For example, during a natural disaster, misinformation might spread regarding the severity of the event or the availability of emergency services. This could lead to panic and confusion among the affected population.
Disinformation

Disinformation, on the other hand, is deliberately created and spread false information with the intent to deceive and manipulate. It is a more malicious form of misinformation, often crafted and disseminated by individuals, groups, or even state-sponsored actors with specific agendas. Disinformation is designed to mislead, distort reality, and influence public opinion.
A classic example of disinformation is the spread of fake news during elections. Malicious actors create and share fabricated stories or manipulate existing news to favor a particular political candidate or cause. These stories are often designed to appeal to emotions and exploit people's biases, leading to a distorted perception of reality.
The Impact of Disinformation and Misinformation

Both disinformation and misinformation can have far-reaching consequences on individuals, communities, and societies as a whole. Here are some key impacts:
Erosion of Trust

When false information spreads, it undermines trust in institutions, media, and even personal relationships. People may become skeptical and hesitant to believe any information, leading to a breakdown of social cohesion and a sense of uncertainty.
Misguided Decisions

Individuals who fall victim to disinformation or misinformation may make poor decisions based on false premises. This can range from personal choices, such as health-related decisions, to larger-scale issues like voting in elections or supporting certain policies.
Social and Political Divides

Disinformation, in particular, has the potential to exacerbate social and political tensions. By spreading false narratives, it can fuel existing biases and create divisions within communities. This can lead to conflicts, polarisation, and a breakdown of democratic processes.
Economic and Security Risks

In some cases, disinformation and misinformation can have severe economic and security implications. For instance, spreading false rumors about a company's financial stability can lead to stock market crashes and significant financial losses. Additionally, disinformation related to national security issues can undermine trust in government institutions and create vulnerabilities.
Identifying Disinformation and Misinformation
Being able to recognize and identify disinformation and misinformation is crucial in today's information landscape. Here are some key indicators to look out for:
- Headlines and Sensationalism: Disinformation often relies on sensational headlines and emotional appeals to grab attention. Be cautious of articles with exaggerated or shocking claims.
- Lack of Credible Sources: Check if the information is supported by reliable sources and experts in the field. If the article lacks citations or relies solely on anonymous sources, it may be suspect.
- Confirmation Bias: We tend to seek out information that confirms our existing beliefs. Be aware of your own biases and question information that aligns too closely with your preconceived notions.
- Reputable Fact-Checking Websites: Utilize trusted fact-checking websites to verify the accuracy of information. These websites employ professional journalists and researchers to debunk false claims.
- Multiple Perspectives: Seek out diverse sources and perspectives on a particular issue. If multiple reputable sources are reporting the same information, it is more likely to be accurate.
Combating Disinformation and Misinformation

While it can be challenging to completely eradicate disinformation and misinformation, there are steps individuals and societies can take to mitigate their impact:
- Media Literacy Education: Promoting media literacy in schools and communities can help individuals develop critical thinking skills and become more discerning consumers of information.
- Fact-Checking Initiatives: Supporting and promoting independent fact-checking organizations can help provide a reliable source of information and hold those spreading false narratives accountable.
- Platform Responsibility: Social media platforms and online publishers have a responsibility to moderate content and remove disinformation. They can implement policies and algorithms to identify and flag misleading information.
- Diverse Media Consumption: By exposing ourselves to a variety of media sources and perspectives, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of issues and be less susceptible to biased or false information.
- Reporting and Flagging: If you come across disinformation or misinformation, report it to the relevant platforms or authorities. By doing so, you can help prevent the spread of false information.
Conclusion

In a world where information is abundant and easily accessible, it is our responsibility to be vigilant and discerning consumers of news and information. By understanding the differences between disinformation and misinformation, recognizing their impacts, and taking proactive steps to identify and combat them, we can contribute to a more informed and resilient society. Let's embrace media literacy, fact-checking, and critical thinking as essential tools in our fight against the spread of false narratives.
FAQ

What is the main difference between disinformation and misinformation?
+
The key difference lies in the intent behind the information. Misinformation is unintentionally shared false information, while disinformation is deliberately created and spread false information with the intent to deceive and manipulate.
How can I spot disinformation online?

+
Look for sensational headlines, lack of credible sources, and information that aligns with your biases. Verify the information with reputable fact-checking websites and seek multiple perspectives.
What are the potential consequences of disinformation and misinformation?

+
Disinformation and misinformation can lead to erosion of trust, misguided decisions, social and political divides, and economic and security risks. They can undermine democratic processes and create a sense of uncertainty and confusion.
How can I contribute to combating disinformation and misinformation?

+
Promote media literacy, support fact-checking initiatives, and encourage diverse media consumption. Report disinformation and misinformation to the relevant platforms and authorities. By taking these steps, we can collectively make a difference.